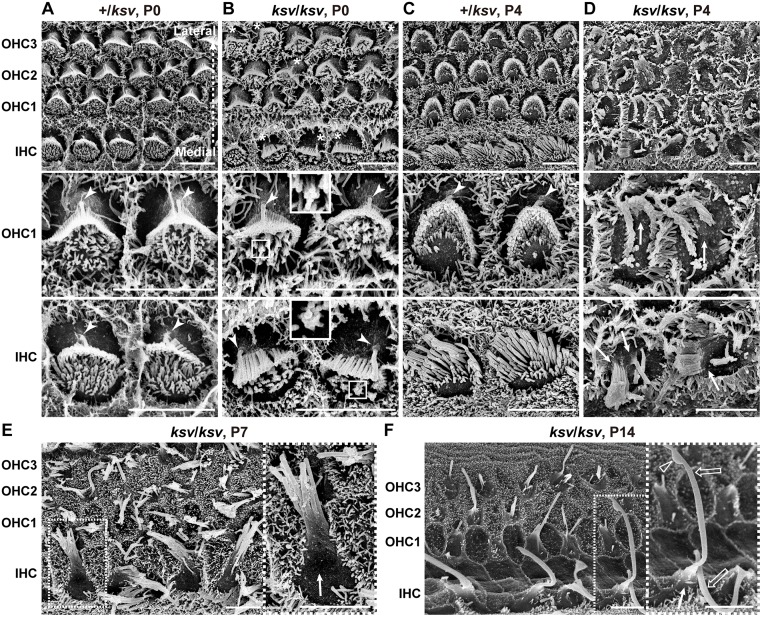
Fig 7. Rapidly progressive stereociliary fusion of the cochlear hair cells in ksv/ksv mice during early postnatal stages.
A–D. Comparison of stereociliary phenotypes between the +/ksv heterozygous (A and C) and ksv/ksv homozygous (B and D) mice at P0 (A and B) and P4 (C and D). SEM images showing stereocilia in the hair cells from the middle area of the cochlea. Highly magnified images of the OHCs (middle panels) and IHCs (bottom panels) are shown. The arrowheads and arrows indicate the kinocilia and bulging basal region of the stereocilia, respectively. The bundling of the stereocilia in both the OHCs and IHCs of ksv/ksv mice at P0 are magnified (white boxes). E. Stereociliary phenotypes in the hair cells from the middle area of the cochlea in ksv/ksv mouse at P7. The highly magnified image (right panel) in the white dotted box in the left panel shows the bulging basal region (arrow) in the fused stereocilia in IHCs. F. Stereociliary phenotypes in the hair cells from the apex area of the cochlea in a ksv/ksv mouse at P14. The highly magnified image (right panel) in the white dotted box in the left panel shows the bulging basal region (arrow) and bulbous tip (open arrowhead) in the elongated giant stereocilia (open arrows) of the IHCs. Scale bars = 5 μm.