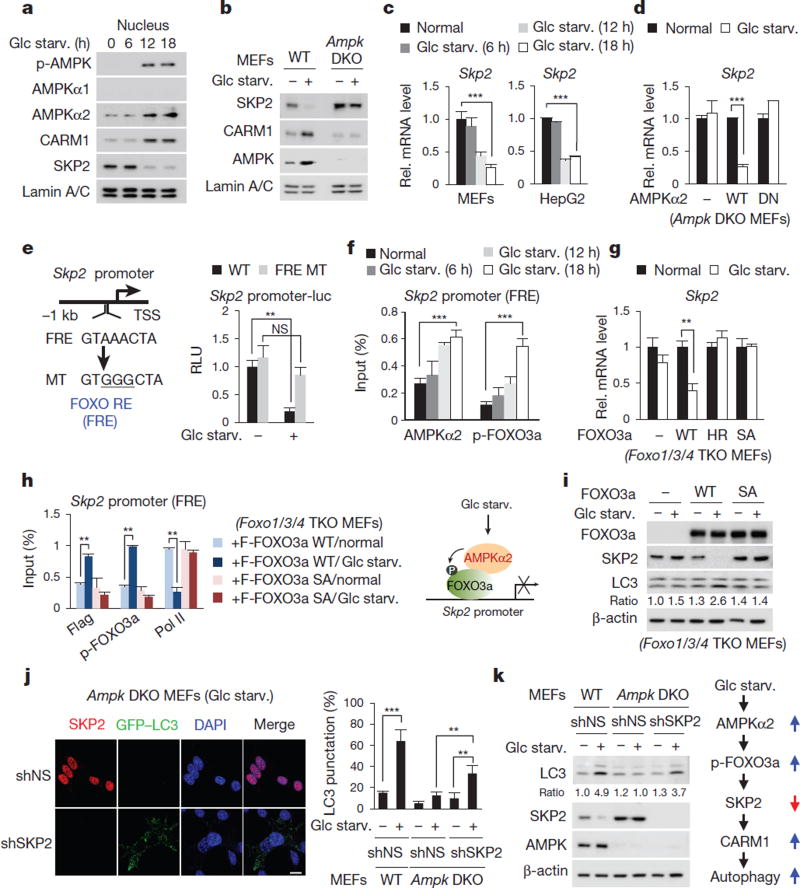
Figure 3. Decrease in SKP2 after glucose starvation is AMPK dependent.
a, MEFs deprived of glucose were analysed with the indicated antibodies. b, Nuclear fractions from wild-type and Ampk double knockout (DKO) MEFs were subjected to immunoblotting. c, d, qRT–PCR of Skp2. DN, dominant negative. e, Left, schematic of Skp2 promoter. Right, luciferase activities of wild-type Skp2 or FOXO response element (FRE) mutant promoter were measured. MT, mutant; RE, response element; RLU, relative light units; TSS, transcription start site. f, ChIP assays of the Skp2 promoter. g, Skp2 mRNA levels were analysed in Foxo1/3/4 triple knockout (TKO) MEFs. HR, H212R mutant; SA, sextuple T179A/ S399A/ S413A/S555A/S588A/S626A mutant. h, Left, ChIP assays of the Skp2 promoter. Right, schematic of SKP2 regulation by the AMPK–FOXO axis (right). Bars, mean ± s.e.m.; n = 3. NS, not significant. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-tailed t-test) (c–h). i, Immunoblot analysis in Foxo1/3/4 TKO MEFs. j, Representative confocal images of GFP–LC3 puncta formation. shSKP2, short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) against SKP2; shNS, nonspecific shRNA. Scale bar, 20 µm. Bars, mean ± s.e.m.; n = 5, with over 80 cells; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-tailed t-test). k, Left, immunoblot analysis from whole-cell extracts. Right, schematic of the AMPK–SKP2–CARM1 signalling cascade in autophagy.