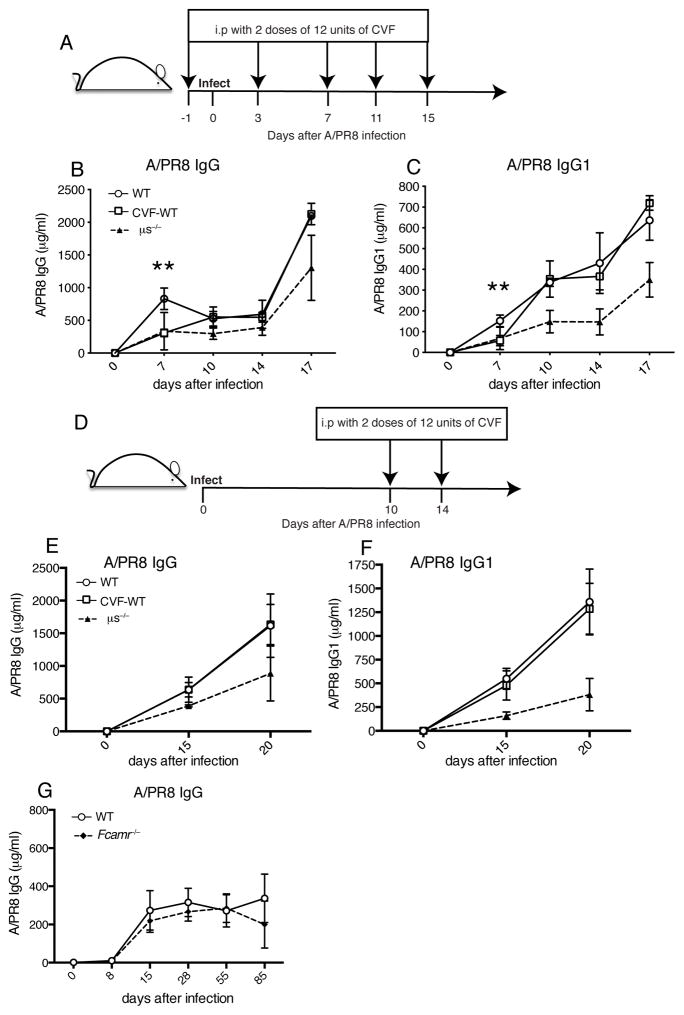
Figure 4. Neither complement depletion nor the lack of Fcα/μR results in long-term effects on antiviral IgG production.
(A) Mice were injected i.p twice with 12 units CVF at day 1 before infection, and days 3, 7, 11, 15 after infection with influenza A/PR8. (B/C) Graphs summarize the levels of (B) A/PR8 specific IgG and (C) IgG1 in sera at indicated times after infection (n=3–4 mice/group). (D) Mice were injected i.p twice with 12 units CVF at days 10 and 14 after infection with influenza A/PR8. (E/F) Levels of (E) A/PR8 specific IgG and (F) IgG1 in sera at indicated times (n=3 mice/group). (G) Mean concentrations ± SD of A/PR8 specific IgG in WT and Fcamr−/− sera after infection (n=4–6 mice/group). *p<0.05, **p<0.005 A/PR8 specific IgG and IgG1 levels between WT mice with and without CVF treatment group, and between WT and Fcamr−/− mice as assessed by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test.