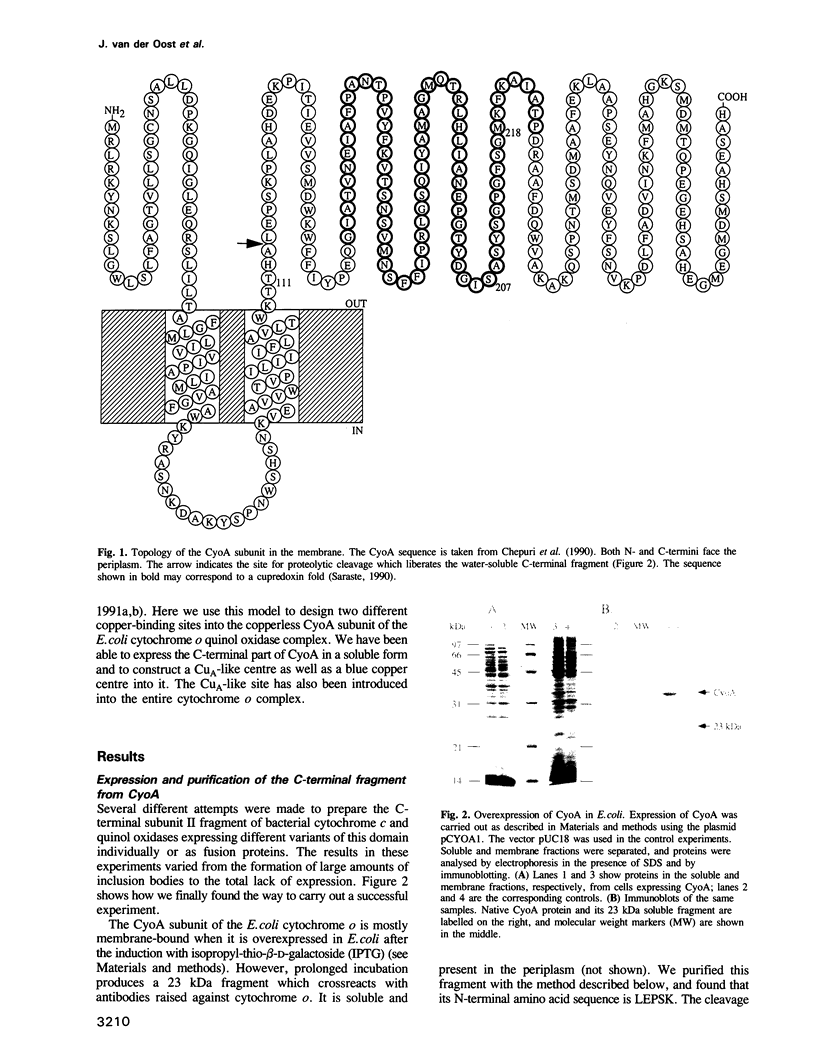
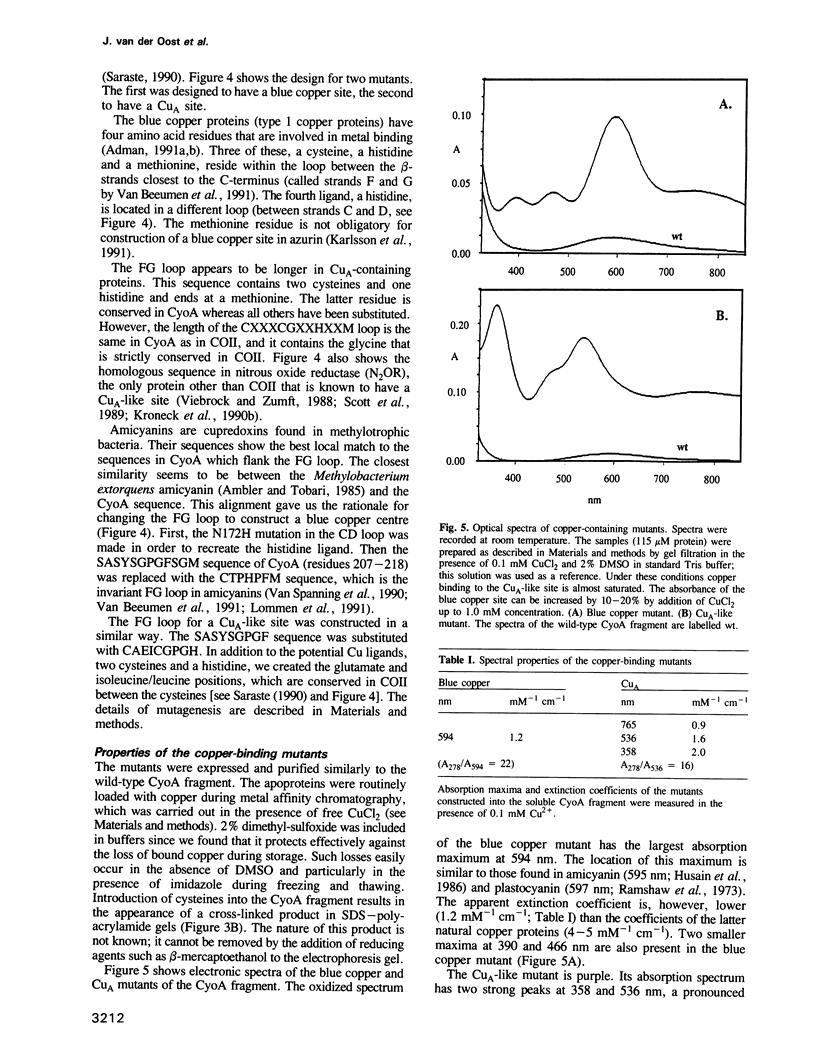
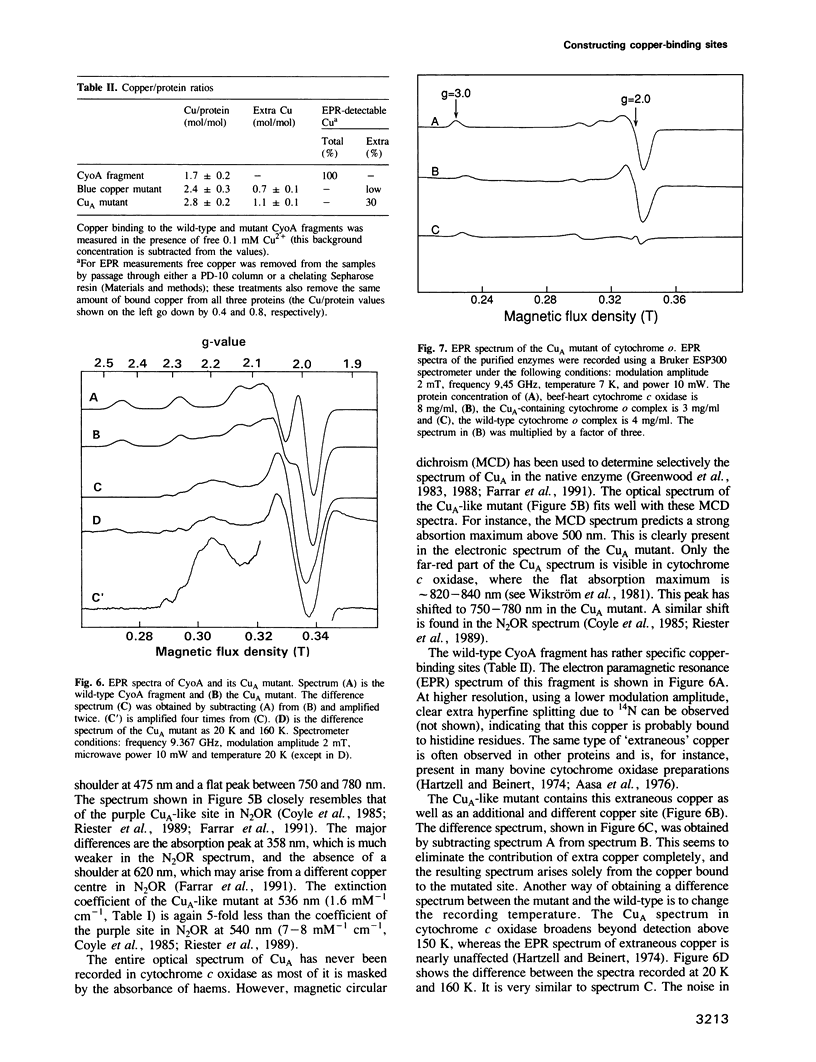
Abstract
The cupredoxin fold, a Greek key beta-barrel, is a common structural motif in a family of small blue copper proteins and a subdomain in many multicopper oxidases. Here we show that a cupredoxin domain is present in subunit II of cytochrome c and quinol oxidase complexes. In the former complex this subunit is thought to bind a copper centre called CuA which is missing from the latter complex. We have expressed the C-terminal fragment of the membrane-bound CyoA subunit of the Escherichia coli cytochrome o quinol oxidase as a water-soluble protein. Two mutants have been designed into the CyoA fragment. The optical spectrum shows that one mutant is similar to blue copper proteins. The second mutant has an optical spectrum and redox potential like the purple copper site in nitrous oxide reductase (N2OR). This site is closely related to CuA, which is the copper centre typical of cytochrome c oxidase. The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra of both this mutant and the entire cytochrome o complex, into which the CuA site has been introduced, are similar to the EPR spectra of the native CuA site in cytochrome oxidase. These results give the first experimental evidence that CuA is bound to the subunit II of cytochrome c oxidase and open a new way to study this peculiar copper site.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasa R., Albracht P. J., Falk K. E., Lanne B., Vänngard T. EPR signals from cytochrome c oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 13;422(2):260–272. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90137-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adman E. T. Copper protein structures. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:145–197. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambler R. P., Tobari J. The primary structures of Pseudomonas AM1 amicyanin and pseudoazurin. Two new sequence classes of blue copper proteins. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 1;232(2):451–457. doi: 10.1042/bj2320451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROMAN L., MALMSTROM B. G., AASA R., VANNGARD T. Quantitative electron spin resonance studies on native and denatured ceruloplasmin and laccase. J Mol Biol. 1962 Sep;5:301–310. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80074-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock G. T., Wikström M. Oxygen activation and the conservation of energy in cell respiration. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):301–309. doi: 10.1038/356301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capaldi R. A., Darley-Usmar V., Fuller S., Millett F. Structural and functional features of the interaction of cytochrome c with complex III and cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1982 Feb 8;138(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. I., Li P. M. Cytochrome c oxidase: understanding nature's design of a proton pump. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):1–12. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
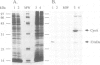
- Chepuri V., Gennis R. B. The use of gene fusions to determine the topology of all of the subunits of the cytochrome o terminal oxidase complex of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12978–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepuri V., Lemieux L., Au D. C., Gennis R. B. The sequence of the cyo operon indicates substantial structural similarities between the cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase of Escherichia coli and the aa3-type family of cytochrome c oxidases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11185–11192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle C. L., Zumft W. G., Kroneck P. M., Körner H., Jakob W. Nitrous oxide reductase from denitrifying Pseudomonas perfectomarina. Purification and properties of a novel multicopper enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Dec 16;153(3):459–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. A., Thomson A. J., Cheesman M. R., Dooley D. M., Zumft W. G. A model of the copper centres of nitrous oxide reductase (Pseudomonas stutzeri). Evidence from optical, EPR and MCD spectroscopy. FEBS Lett. 1991 Dec 2;294(1-2):11–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenderson F. F., Kumar S., Adman E. T., Liu M. Y., Payne W. J., LeGall J. Amino acid sequence of nitrite reductase: a copper protein from Achromobacter cycloclastes. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7180–7185. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Hill B. C., Barber D., Eglinton D. G., Thomson A. J. The optical properties of CuA in bovine cytochrome c oxidase determined by low-temperature magnetic-circular-dichroism spectroscopy. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):303–316. doi: 10.1042/bj2150303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood C., Thomson A. J., Barrett C. P., Peterson J., George G. N., Fee J. A., Reichardt J. Some spectroscopic views of the CuA site in cytochrome c oxidase preparations. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;550:47–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb35321.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell C. R., Beinert H. Components of cytochrome c oxidase detectable by EPR spectroscopy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 19;368(3):318–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L., Saraste M., Wikström M. Structural models of the redox centres in cytochrome oxidase. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2819–2823. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02578.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain M., Davidson V. L., Smith A. J. Properties of Paracoccus denitrificans amicyanin. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2431–2436. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson B. G., Nordling M., Pascher T., Tsai L. C., Sjölin L., Lundberg L. G. Cassette mutagenesis of Met121 in azurin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Eng. 1991 Feb;4(3):343–349. doi: 10.1093/protein/4.3.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroneck P. M., Antholine W. A., Riester J., Zumft W. G. The cupric site in nitrous oxide reductase contains a mixed-valence [Cu(II),Cu(I)] binuclear center: a multifrequency electron paramagnetic resonance investigation. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):70–74. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80987-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroneck P. M., Antholine W. E., Kastrau D. H., Buse G., Steffens G. C., Zumft W. G. Multifrequency EPR evidence for a bimetallic center at the CuA site in cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):274–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81026-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroneck P. M., Riester J., Zumft W. G., Antholine W. E. The copper site in nitrous oxide reductase. Biol Met. 1990;3(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01179514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauraeus M., Haltia T., Saraste M., Wikström M. Bacillus subtilis expresses two kinds of haem-A-containing terminal oxidases. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 8;197(3):699–705. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux L. J., Calhoun M. W., Thomas J. W., Ingledew W. J., Gennis R. B. Determination of the ligands of the low spin heme of the cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase complex using site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2105–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lommen A., Wijmenga S., Hilbers C. W., Canters G. W. Assignment of the 600-MHz 1H-NMR spectrum of amicyanin from Thiobacillus versutus by two-dimensional NMR methods provides information on secondary structure. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 1;201(3):695–702. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16330.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübben M., Kolmerer B., Saraste M. An archaebacterial terminal oxidase combines core structures of two mitochondrial respiratory complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):805–812. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05117.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmström B. G. Cytochrome oxidase: some unsolved problems and controversial issues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Aug 1;280(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90325-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. T., Scholes C. P., Chan S. I. On the nature of cysteine coordination to CuA in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8420–8429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messerschmidt A., Huber R. The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15311.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minagawa J., Mogi T., Gennis R. B., Anraku Y. Identification of heme and copper ligands in subunit I of the cytochrome bo complex in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):2096–2104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oblad M., Selin E., Malmström B., Strid L., Aasa R., Malmström B. G. Analytical characterization of cytochrome oxidase preparations with regard to metal and phospholipid contents, peptide composition and catalytic activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 13;975(2):267–270. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(89)80257-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan L. P., Li Z. Y., Larsen R., Chan S. I. The nature of Cux in cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1367–1370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puustinen A., Finel M., Haltia T., Gennis R. B., Wikström M. Properties of the two terminal oxidases of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3936–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puustinen A., Finel M., Virkki M., Wikström M. Cytochrome o (bo) is a proton pump in Paracoccus denitrificans and Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jun 5;249(2):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80616-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitio M., Jalli T., Saraste M. Isolation and analysis of the genes for cytochrome c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2825–2833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw J. A., Brown R. H., Scawen M. D., Boulter D. Higher plant plastocyanin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 20;303(2):269–273. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riester J., Zumft W. G., Kroneck P. M. Nitrous oxide reductase from Pseudomonas stutzeri. Redox properties and spectroscopic characterization of different forms of the multicopper enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):751–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén L. Model of the active site in the blue oxidases based on the ceruloplasmin-plastocyanin homology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6767–6771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santana M., Kunst F., Hullo M. F., Rapoport G., Danchin A., Glaser P. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and physiological characterization of the qox operon from Bacillus subtilis encoding the aa3-600 quinol oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10225–10231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Holm L., Lemieux L., Lübben M., van der Oost J. The happy family of cytochrome oxidases. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Aug;19(3):608–612. doi: 10.1042/bst0190608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M. Structural features of cytochrome oxidase. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Nov;23(4):331–366. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. A., Zumft W. G., Coyle C. L., Dooley D. M. Pseudomonas stutzeri N2O reductase contains CuA-type sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4082–4086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G. C., Biewald R., Buse G. Cytochrome c oxidase is a three-copper, two-heme-A protein. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 15;164(2):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11057.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G. J., Buse G. Studies on cytochrome c oxidase, IV[1--3]. Primary structure and function of subunit II. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Apr;360(4):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beeumen J., Van Bun S., Canters G. W., Lommen A., Chothia C. The structural homology of amicyanin from Thiobacillus versutus to plant plastocyanins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4869–4877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. M., Herron J. N., Voss E. W., Jr First order dissociation rates between a subpopulation of high affinity rabbit anti-fluorescyl IgG antibody and homologous ligand. Mol Immunol. 1980 Oct;17(10):1237–1243. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Spanning R. J., Wansell C. W., Reijnders W. N., Oltmann L. F., Stouthamer A. H. Mutagenesis of the gene encoding amicyanin of Paracoccus denitrificans and the resultant effect on methylamine oxidation. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Kamp M., Hali F. C., Rosato N., Agro A. F., Canters G. W. Purification and characterization of a non-reconstitutable azurin, obtained by heterologous expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa azu gene in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 19;1019(3):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90206-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]