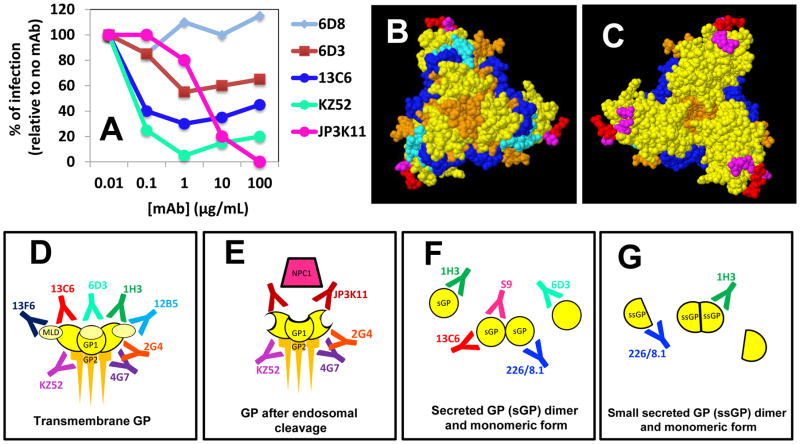
Figure 4.
Different mAbs bind to different GP epitopes and interfere at different functional levels. (A) A plot of the percentages of infection inhibition (in vitro) at different mAb concentrations for five different anti-GP mAbs (data modified from Sheldock et al. 2010); (B) Bottom and (C) top view of the chalice of the GP trimer. The epitopes for selected anti-GP mAbs have been indicated with different colors: S9 (red); 1H3 (magenta); JP3K11 (light blue); 133/3.16 (blue). (D) Some mAbs bind to transmembrane GP (E), and/or the enzymatically cleaved form of GP; (F) and/or the monomeric or dimmer versions of sGP (the secreted form of GP) and (G) ssGP.