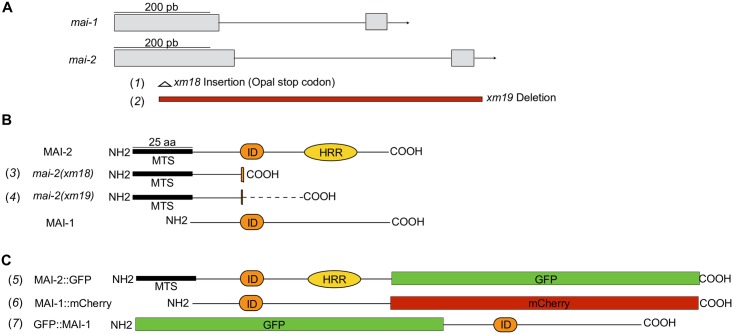
Fig 1. Alleles and translational reporters used to study the function of mitochondria ATPase inhibitors in C. elegans.
(A) The mai-1 and mai-2 genes are composed of 2 exons (gray rectangles) and one intron (thin line). (B) We generated two mutant alleles, mai-2(xm18) and mai-2(xm19), by CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing. Both mutant alleles encode two truncated MAI-2 proteins that conserve the mitochondrial targeting sequence (MTS) but lack the inhibitory domain (ID) and histidine-rich region (HRR), which are essential for MAI-2 function and regulation (3,4). The dotted line (—) in the mai-2(xm19) product represents a randomly formed sequence of amino acids (4). (C) To study protein localization, we generated translational reporters for MAI-1 and MAI-2 (5–7). We inserted, in the carboxyl-terminal, a GFP construct for MAI-2 (5); for MAI-1, we inserted a carboxy-terminal mCherry (6) and an amino-terminal GFP (7).