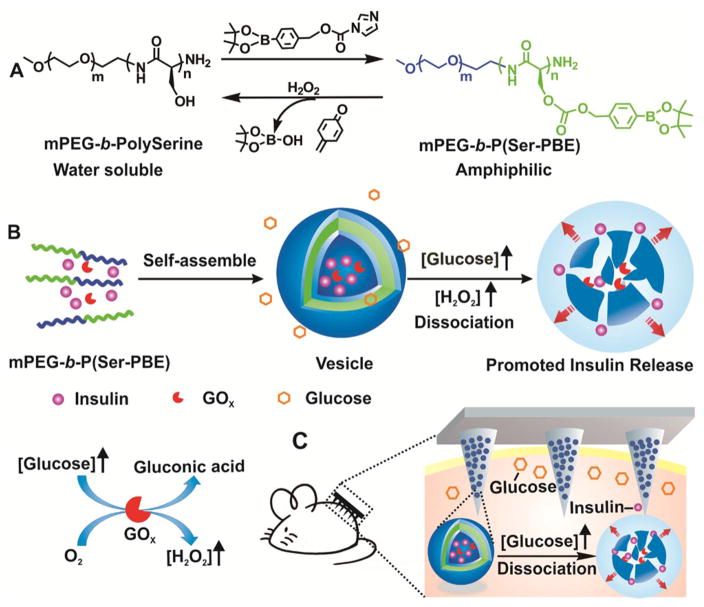
Figure 1.
Schematic of the H2O2-responsive vesicles for glucose-mediated insulin delivery: (A) chemical structure of mPEG-b-P(Ser-PBE) and its degradation products; (B) self-assembly of block copolymer mPEG-b-P(Ser-PBE) into vesicles loaded with insulin and GOx. The vesicles are dissociated to release insulin in the presence of a hyperglycemic state; (C) PVs were further integrated into the hyaluronic acid (HA)-based microneedle-array patches for smart insulin delivery in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes.