Figure 2.
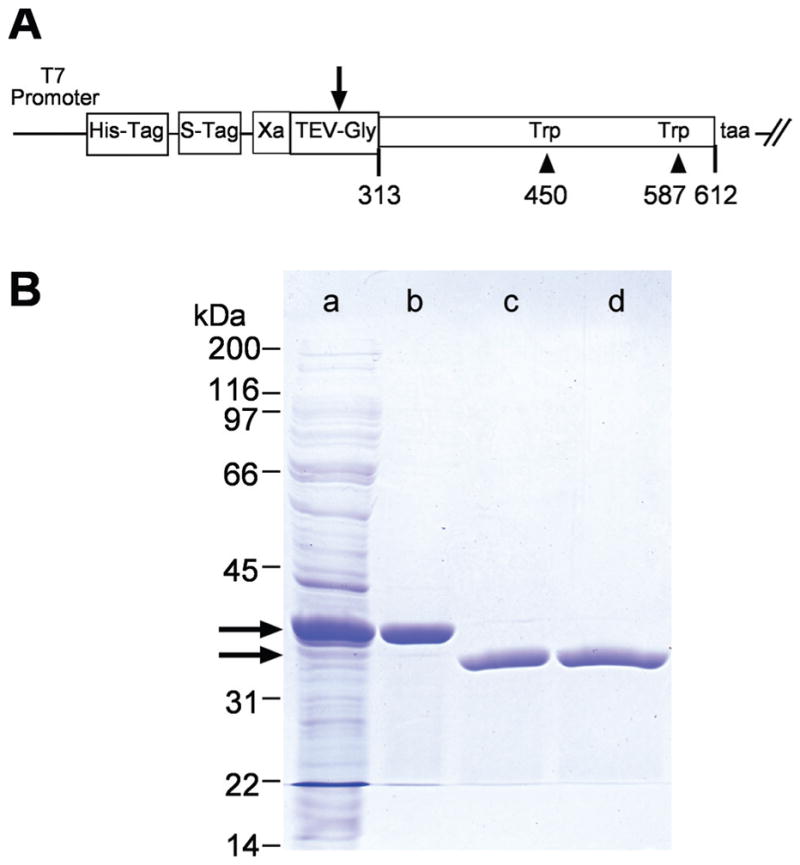
X2IRBP and the W450T and W587T mutants were expressed in a soluble form as polyhistidine-fusion proteins. The fusion domain was removed by cleavage with tobacco-etch virus (TEV) protease. (A) Map of the plasmid construct used to express the wild-type and mutant forms of X2IRBP. Arrow: cleavage site in the TEV protease recognition site (GluAsnLeuTyrPheGln ↓ Gly). Amino-acid residues are numbered according to the sequence of the full-length Xenopus IRBP. (B) Purification of X2IRBP and removal of its polyhistidine fusion tag. Lane a: total soluble E. coli lysate. Lane b: proteins binding to the HisTrap-nickel column. Lane c: Proteins not binding to a second HisTrap column after TEV cleavage. Lane d: Cleaved X2IRBP following Q-Sepharose HP ion-exchange chromatography. Arrows: positions of the fusion protein before and after TEV cleavage, respectively. Protein size standards are shown on the left of the gel. SDS (4%–20% gradient)-polyacrylamide gel stained with Coomassie blue.
