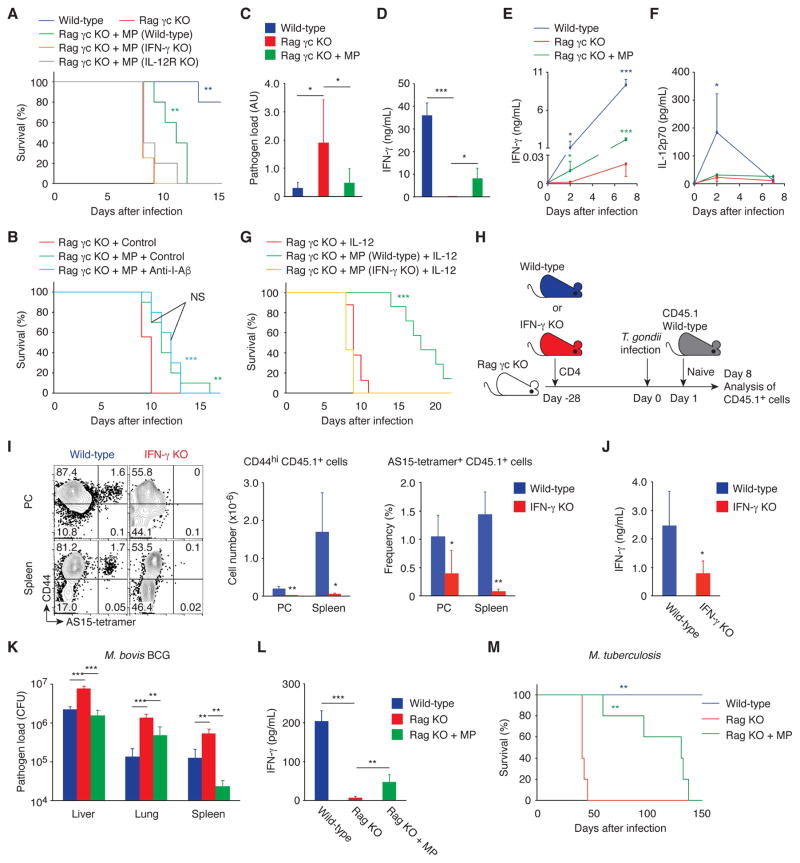
Fig. 8. MP cells can mediate resistance in infectious models that induce Th1-type immunity.
(A to G) MP cells ameliorate toxoplasmosis via the IL-12-IFN-γ axis in the absence of pathogen antigen recognition. (A) Survival of T. gondii-infected wild-type, Rag γc KO, and Rag γc KO animals that had received CD4+ T cells from wild-type, IFN-γ KO, or IL-12Rβ2 KO mice 4 weeks earlier was monitored daily (n=4–5). (B) T. gondii-infected Rag γc KO and Rag γc KO mice with MP cells were treated with anti-I-Aβ mAb or control IgG and survival was assessed (n=9–10). (C) The relative pathogen load (mean ± SD) and (D) concentration of IFN-γ in PC of T. gondii-infected wild-type, Rag γc KO, and Rag γc KO animals that received CD4+ T cells 4 weeks earlier (n=3–10). (E and F) Serum IFN-γ and IL-12p70 concentration (mean ± SD) at the indicated days after infection (n=3–5). (G) T. gondii-infected Rag γc KO mice with or without MP cells from wild-type or IFN-γ KO mice were treated with IL-12 and survival was assessed (n=7–8). Data shown are (A, D to F) representative of 2, (B, C) pooled from 2, and (G) pooled from 3 independent experiments performed. (H to J) IFN-γ produced by MP cells augments antigen-specific effector CD4+ T cell responses. (H) Experimental design. Rag γc KO mice that had received CD4+ T cells from wild-type or IFN-γ KO mice at day -28 were infected with T. gondii at day 0 and transferred with sorted naïve CD4+ T cells from CD45.1 mice at day 1. (I) The representative dot plots show CD44 expression versus AS15-tetramer staining by CD45.1 donor cells from each group at day 8, while the bar graphs show the number (mean ± SD) of CD44hi CD45.1 donor cells (left) and the frequency (mean ± SD) of CD44hi AS15-tetramer+ cell population among CD45.1 donor cells (right, n=5). (J) CD44hi CD62Llo CD45.1 donor cell population sorted from splenocytes of each group was stimulated with STAg. The bar graph shows the concentration (mean ± SD) of IFN-γ in the culture supernatant from each group (n=4–5). (K and L) MP cells produce IFN-γ and control bacterial growth in M. bovis BCG infection. Wild-type, Rag KO, and Rag KO mice that had received CD4+ T cells 4 weeks earlier were infected with M. bovis BCG and (K) bacterial burden (CFU, mean ± SD) in the indicated organs and (L) concentration (mean ± SD) of IFN-γ in the spleen were analyzed 17 days after infection (n=4–5). (M) MP cells are protective in M. tuberculosis infection. Wild-type, Rag KO, and Rag KO mice that had received CD4+ T cells were infected with M. tuberculosis and survival was assessed (n=5). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, NS not significant.