Figure 6.
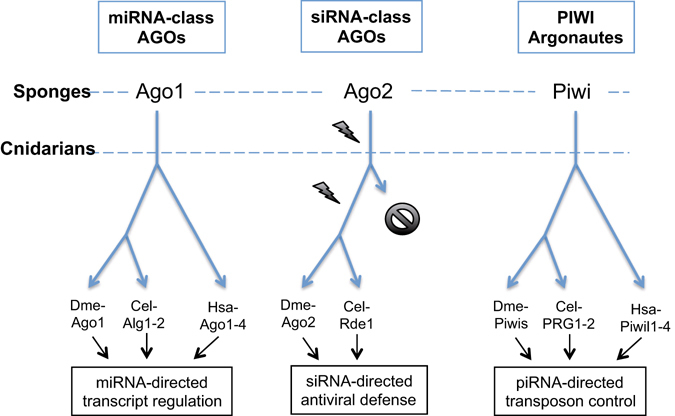
The evolution of the metazoan Argonaute superfamily. The miRNA-class AGO, siRNA-class AGO and PIWI Argonaute lineages are conserved between sponges, cnidarians, nematodes and insects, while chordates only encode miRNA-class AGOs and PIWIs (the absence of the siRNA-class AGOs in vertebrates is depicted by a black stop sign). Several studies have identified that the miRNA-class AGOs in the fruit fly (Dme-Ago1), C. elegans (Cel-ALG1-2) and humans (Hsa-Ago1-4) can interact with miRNAs and mediate regulation of endogenous transcripts (indicated with black arrows), the siRNA-class AGOs of flies (Dme-Ago2) and C. elegans (Cel-RDE-1) play a crucial role in the defense against viruses (black arrows), and finally, the PIWI Argonautes in flies (Dme-Piwis: Ago3, Piwi and Aubergene), C. elegans (Cel-PRG1-2) and humans (Hsa-Piwil1-4) mediate piRNA-directed control of transposons (also depicted by black arrows). The siRNA-class AGOs are characterized by elevated rates of molecular evolution (depicted by lightning signs).
