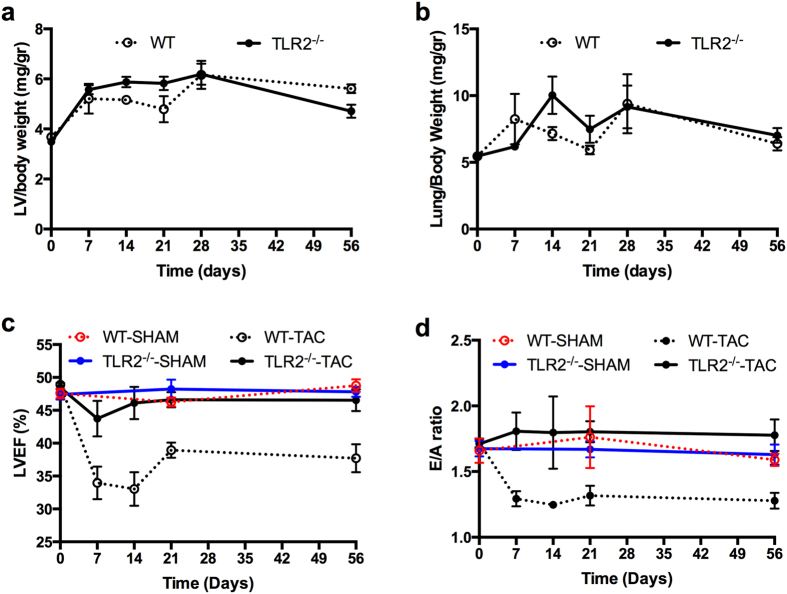
Figure 1.
Left ventricle weight, lung weight and cardiac function after sustained pressure overload. (a,b) Mouse LV and lungs were extracted before TAC (baseline, n = 10–12 per genotype), or 7 days (n = 6–7 per genotype), 14 days (n = 8–10 per genotype), 21 days (n = 6 per genotype), 28 days (n = 6–9 per genotype) and 56 days (n = 21–26 per genotype) after TAC from WT and TLR2−/− mice. Wet LV weight and lung weight were corrected for body weight. No significant differences in LV or lung weight between WT and TLR2−/− mice were detected. (c,d) LVEF as an indicator for cardiac systolic function and E/A ratio as an indicator for cardiac diastolic function were determined with echocardiography at indicated timepoints after TAC. N = 14 for WT-SHAM, n = 12 for TLR2−/−-SHAM, n = 26 for WT-TAC and n = 22 for TLR2−/−-TAC. GLM model analysis was performed, p < 0.0001 between WT-TAC and TLR2−/−-TAC.