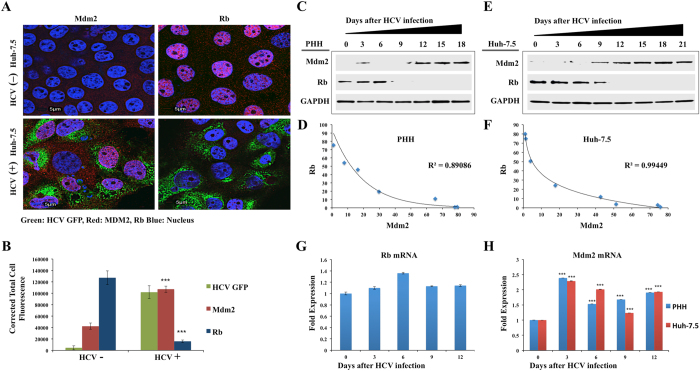
Figure 5.
Persistent HCV replication induces Mdm2-mediated degradation of Rb tumor suppressor. (A) Colocalization studies by confocal microscopy between HCV-GFP and nuclear expression of Mdm2 and Rb in infected Huh-7.5 cells at day 12. (B) Fluorescence intensity of three areas was measured by ImageJ software, indicating HCV infection induces Mdm2 but degrades Rb. (C) Cell lysates were prepared from infected PHHs at indicated time points, and were examined for the expression of Mdm2 and Rb by Western blotting. GAPDH levels were examined for comparison. (D) Band intensities of Mdm2 and Rb were measured using ImageJ software andR2 values were determined by excel software. (E) The expressions of Rb and Mdm2 were measured in the infected Huh-7.5 cells at indicated time points by Western blotting. (F) Band intensities of Mdm2 and Rb were measured using ImageJ software and R2 values were determined by excel software. (G) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of Rb mRNA levels of HCV infected Huh-7.5 cells. Rb forward sequence 5′-GGAAGCAACCCTCCTAAACC-3′, reverse sequence 5′-TTTCTGCTTTTGCATTCGTG -3′. (H) Real-time RT-PCR shows that Mdm2 mRNA levels are induced in HCV infected PHHs and Huh-7.5 cells. Mdm2 forward sequence 5′-TGTAAGTGAACATTCAGGTG-3, reverse sequence 5′-TTCCAATAGTCAGCTAAGGA-3′. ***P value < 0.0001.