Figure 1.
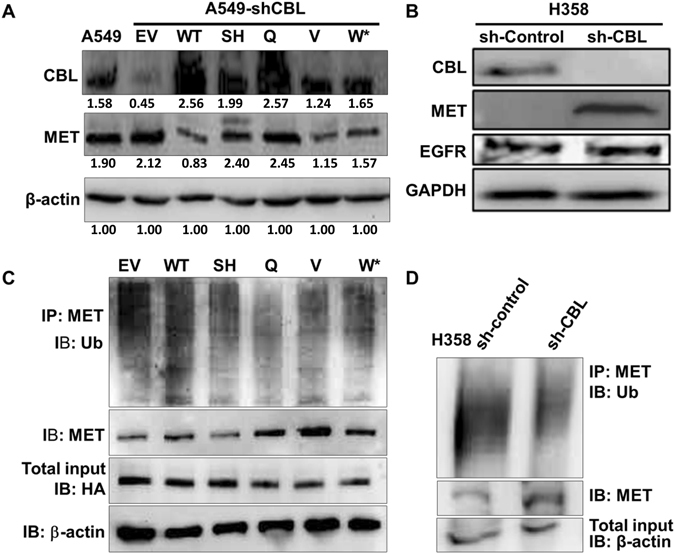
Ubiquitination and expression analysis of various CBL mutants. (A) A549 shRNA knockdown CBL cells were transiently transfected with various CBL mutants (SH: S80N/H94Y, Q: Q249E, V: V391I, W*: W802*) and wild-type (WT). MET protein showed low expression in CBL WT and high expression in CBL Mts isogenic cells. Protein expression was quantified and indicated with the fold change numbers shown below each immunoblot in comparison with loading control β-actin. (B) MET and EGFR expression of H358 sh-control and sh-CBL. MET showed higher expression in sh-CBL than sh-control cells. EGFR had no difference in sh-control and sh-CBL. (C) A549 cells transiently transfected with empty vector (EV) or CBL WT and Mts (SH: S80N/H94Y, Q: Q249E, V: V391I, W*: W802*). Whole cell lysates were IP with anti-MET antibody and IB with anti-Ub antibody. IB with anti-HA antibody for transfection efficiency and β-actin for loading control of the IP. The results showed the ubiquitination of MET were decreased in A549 cells that transiently expressed CBL mutants relative to CBL WT cells. (D) H358 sh-Control and sh-CBL cell lysates were IP with anti-MET antibody and IB with anti-Ub antibody β-actin for loading control of the IP. The results showed the ubiquitination of MET were decreased in sh-CBL cells relative to sh-control cells. Each protein lysates of separated blot of were collected in the same time period for and the lysates were loaded in one gel per antibody staining.
