Figure 1.
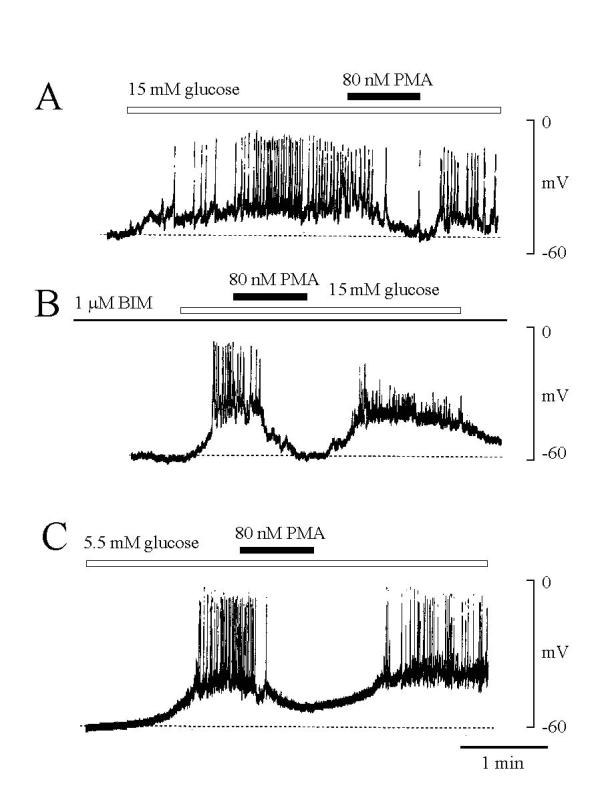
Effect of PMA on electrical excitation of single rat pancreatic β-cells. The membrane potential was measured the nystatin-perforation method. (A) Increases in extracellular glucose concentration from 5.5 to 15 mM induced a slow membrane depolarization superimposed on action potentials. Addition of PMA (80 nM) inhibited action potentials also membrane depolarization. (B) In the cell treated with BIM (1 μM, for one hour), PMA (80 nM) still inhibited extracellular glucose-induced membrane depolarization and action potentials. (C) In the presence of 5.5 mM glucose, some cells (5/8) showed spontaneous electrical excitation, which also inhibited by PMA. The concentration of glucose in the extracellular solution was 5.5 mM. Dotted lines indicate the membrane potential level before stimulation with glucose or PMA. Representative tracings from at least six experiments are shown.
