Figure 7.
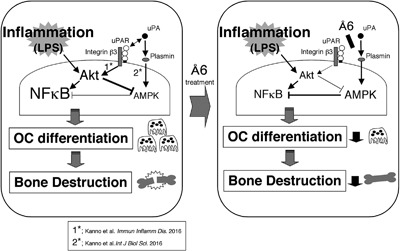
The proposed mechanism of the Å6‐attenuated inflammatory osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction induced by LPS. LPS induced NF‐κB activation, resulting in inflammatory osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction. On the other hand, uPAR and uPA‐activated plasmin activated the Akt and AMPK pathways, respectively. In addition, the uPAR‐induced Akt activation inhibited AMPK pathway. Å6 attenuated the uPAR‐activeted Akt pathway, possibly resulting in the upregulaton of AMPK activation. The resultant suppression of NF‐κB activity inhibited inflammatory osteoclastogenesis and bone destruction.
