Fig. 1.
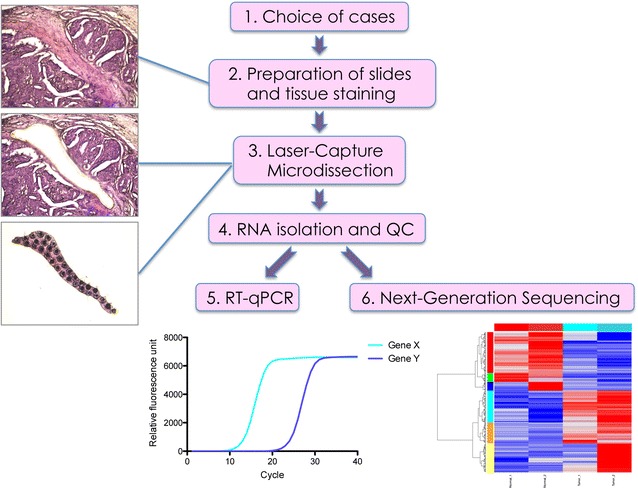
Workflow for the isolation and analysis of RNA from normal and cancer-associated stroma from FFPE tissue by Laser-capture microdissection. (1) Canine simple mammary carcinoma cases to be analysed are chosen from the archives. (2) Sectioning and mounting of FFPE sections is followed by tissue deparaffinisation and staining to visualise structures under the microscope (top panel on the left). (3) Laser-capture microdissection allows excision of areas of interest, and visual validation of the excised area (middle panel on the left) as well as the excised tissue piece (bottom panel on the left). The black spots that appear on the excised tissue piece are a result of the thermoplastic film that is welded to the tissue, and not tissue damage. (4) RNA is isolated from the excised tissue of interest, and quality control is performed to measure RNA quality and quantity. (5) RT-qPCR or (6) NGS can be used to analyse the extracted RNA
