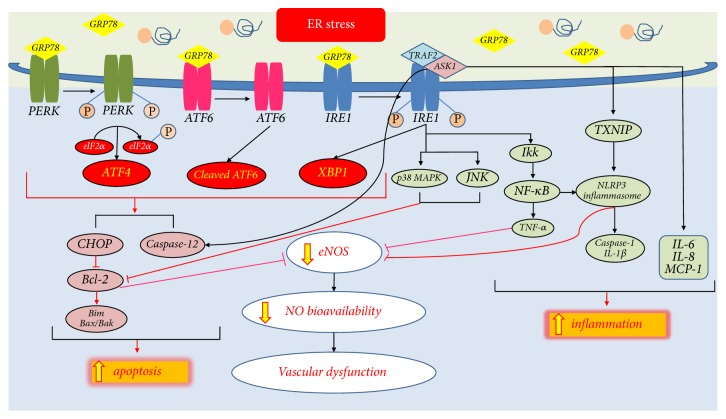
Figure 1.
ER stress-mediated apoptosis and inflammation in cardiovascular disease. When prolonged ER stress occurs, activation of CHOP-mediated and JNK/p38 MAPK-mediated apoptosis signaling pathways regulate the Bcl-2 family, which controls the balance of pro-/antiapoptotic signaling, and ER stress-induced apoptosis signaling dampens eNOS expression with the increased oxidative stress. The IRE1α/TRAF2/ASK1 complex also activates caspase-12 and ultimately induces cell apoptosis. Furthermore, ER stress-mediated NF-κB-IKK activates NLRP3 inflammasome and mediates eNOS activity. Excessive ER stress and activation of the IRE1α/TRAF2/ASK1 pathway increase TXNIP activation that subsequently induces NLRP3 inflammasome and reduced eNOS activity. The IRE1α/TRAF2/ASK1 complex also contributes to the expression of proinflammations that stimulate NLRP3 inflammasome-induced caspase-1 and IL-1β and UPR-mediated IL-6. ER stress also activates IL-8, MCP-1, and TNF-α expression. Ultimately, the accumulation of ER stress-mediated apoptotic and inflammatory responses decreases the eNOS activity which diminishes NO bioavailability and causes vascular dysfunction. The yellow arrows represent ER stress-mediated pathway.