Figure 1.
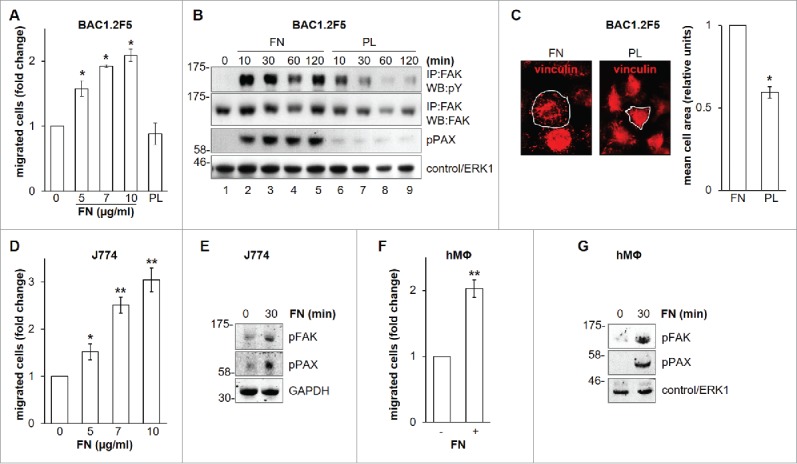
Effects of FN on migration and FAK in macrophages. Dose-response effect of FN on the migration of murine BAC1.2F5 macrophages. (A) Cells were cultured in the absence of CSF-1 for 18 hours and then subjected to migration assay toward DMEM containing or not FN at the indicated concentrations or PL (10 μg/ml). Migrated cells were counted. Histograms represent means ± SEM of data from 4 independent experiments each performed in triplicate. Student's t test: *, p< 0.05 versus untreated. Kinetics of FAK activation induced by FN in BAC1.2F5 cells. (B) Cells were cultured in the absence of CSF-1 for 18 hours, kept in suspension for 45 minutes and then plated on FN- or PL-coated dishes (10 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Protein lysates were then subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) and/or immunoblotting (WB) with the indicated antibodies. Representative images of WB from one out of 3 independent experiments are shown. Molecular weight markers are reported on the left of gels. FN-induced macrophage adhesion. (C) Cells were cultured in the absence of CSF-1 for 18 hours and then let adhere on FN- or PL-coated coverglass (10 μg/ml) for the indicated times. Cells were then stained with anti-vinculin antibodies and analyzed by confocal microscopy. Cell area was then measured. Histograms represent means ± SEM of data from 2 independent experiments. Student's t test: *, p < 0.05 vs. FN. Examples of selected areas are indicated. FN induces macrophage migration and FAK activation in J774 murine macrophages as well as human primary macrophages. (D, F) Migration assay was performed as described in (A). Histograms represent means ± SEM of data from 2 independent experiments each performed in triplicate. Student's t test: *, p < 0.05 versus untreated; **, p < 0.01 vs. untreated. (E, G) Total cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Representative images of WB from one out of 3 (E) or 2 (G) independent experiments are shown. Molecular weight markers are reported on the left of gels.
