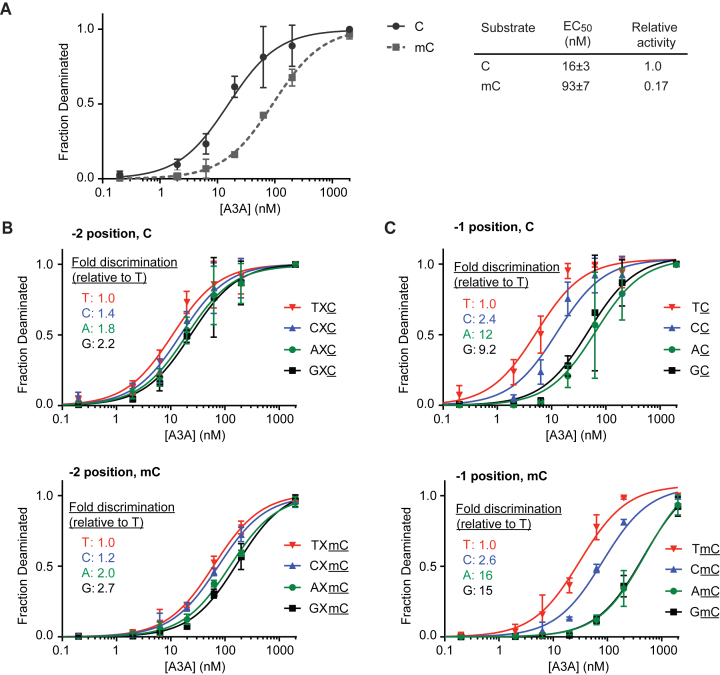
Figure 3.
Deamination of long, single-stranded substrates. (A) A total of 1 ng of single-stranded 636-mer DNA substrates containing either unmodified bases or mC in place of all cytosines were treated with various concentrations of A3A and then were clonally sequenced. Plotted are the fractions of deaminated bases as a function of A3A concentration. Each data point represents the average from at least three independent experiments, with each experiment containing 2–4 clones sequenced under that condition. The standard deviation is calculated between the independent experiments. Both C- and mC-containing substrates can be fully deaminated at the highest concentrations of A3A. The EC50 is the enzyme concentration to achieve 50% deamination of all C or mC bases and was calculated by fitting each curve to a hyperbolic function. The effect of local sequence context was examined by separately analyzing deamination efficiency for (B) the −2 position relative to the target base or (C) the −1 position relative to the target base. Each position is considered independently of the other position, and X denotes any base. The fold discrimination is the ratio of EC50 for a given base, relative to that of the preferred T at the same position.