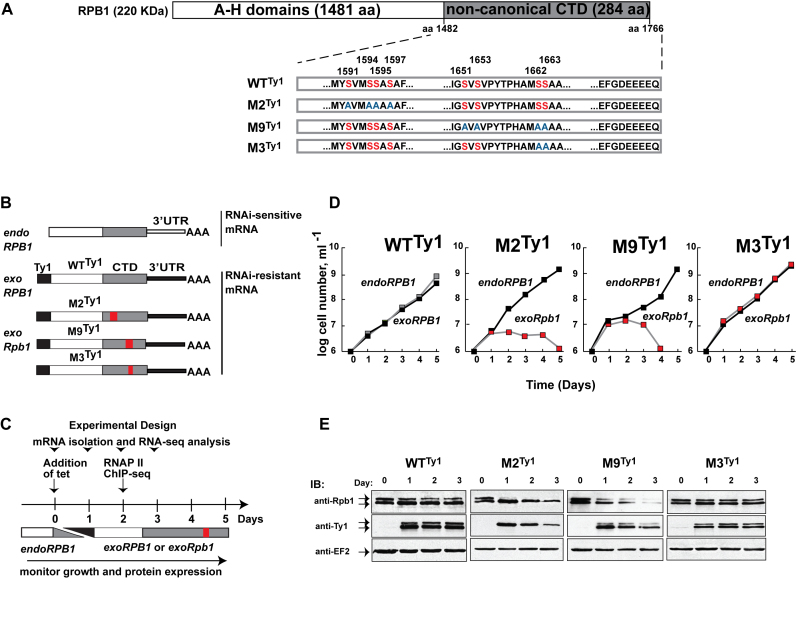
Figure 1.
Mutations in the CTD of T. brucei RPB1 cause varied phenotypes. (A) Schematic of T. brucei RPB1. The conserved A-H domains, characteristic of eukaryotic RNA pol II, make up the body of the polypeptide. They are followed by a 284-amino acid-long non-canonical CTD (gray) in place of the canonical CTD found in most model eukaryotes. Clusters of serine residues (red, numbered on top) in the WTTy1 CTD that were substituted with alanine residues (blue) in the cell lines M2Ty1, M9Ty1 and M3Ty1 are shown. Drawing is not to scale. (B) Schematic of genetic background in four transgenic cell lines. Endogenous RPB1 (endoRPB1) mRNAs, encoded by allelic pairs within chromosomes 4 and 8, contain similar 3΄UTRs (open bar) that are targeted for RNAi-mediated destruction in the presence of tetracycline. N-terminally tagged (black box) proteins are produced from RNAi-resistant mRNA containing a different 3΄UTR (closed bar), also in the presence of tetracycline. Red boxes mark regions containing the serine-to-alanine mutations. (C) Schematic of experimental design for growth and expression analyses. Stable transgenic cell lines were induced with tetracycline on Day 0. Time points indicate days after induction. The gray and black ramps indicate the corresponding decrease of endogenous RPB1 and increase of tagged proteins. (D) Growth curves of WTTy1, M2Ty1, M9Ty1 and M3Ty1 cells in the absence (black squares) and presence (gray/red squares) of tetracycline. Tetracycline addition caused endogenous RPB1 depletion and concomitant production of tagged proteins. (E) Immunoblot analyses of whole cell extracts prepared before (Day 0) and after (Days 1–3) tetracycline induction. Anti-RPB1 antibodies detect both endogenous RPB1 and exogenous wild-type, or mutant, Ty1-tagged RPB1 proteins. Anti-Ty1 antibodies detect only the tagged proteins. Robust expression of tagged protein in each of the cell lines is visible on Day 1. As RPB1 is predicted to have multiple and dynamic modifications, it often appears as a doublet. Anti-EF2 immunoblots are loading controls.