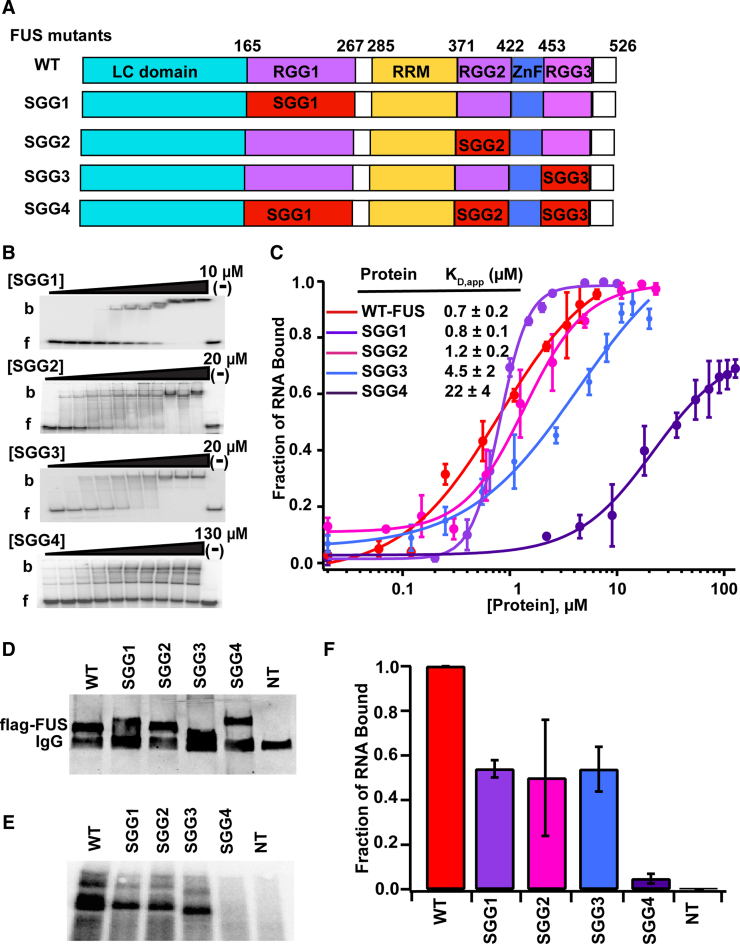
Figure 4.
RGG/RG domains of FUS mediate high affinity binding to RNA. (A) Schematic illustration of RGG/RG domain mutations. Arginine amino acids of individual RGG/RG domains were converted to serine amino acids in SGG1, SGG2 and SGG3 mutants. In SGG4 mutant, arginine amino acids in all RGG/RG domains were converted to serines. (B) Representative EMSAs of mutant FUS proteins with the DNMT RNA and (C) corresponding binding curves. b = bound and f = free. ‘(−)’ shows no protein lane. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent titrations for each construct. (D) Western blot data of flag-tagged, wild-type and mutant FUS constructs expressed in HEK293T cells. (E) SDS-PAGE of radiolabeled RNA fragments cross-linked to flag-tagged FUS or SGG mutants of FUS. (F) Two technical replicates of three separate pull-downs were quantitated and average together. Error bars represent standard deviation.