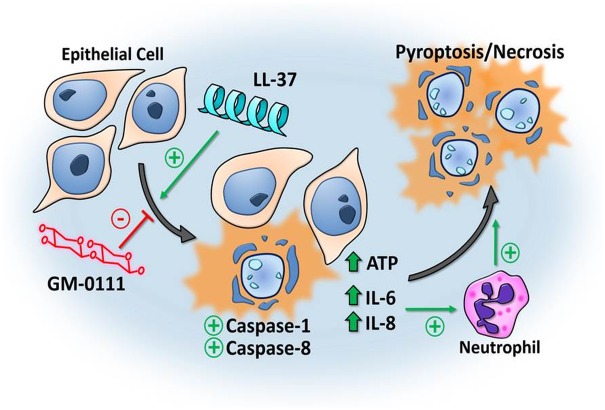
Fig 6. Diagram of the proposed mechanism of LL-37-induced cell death and protection from GM-0111.
Nasal epithelial cells subjected to LL-37 demonstrate a pro-inflammatory response, characterized by increased ATP, IL-6, and -8 production and pyroptosis and/or necrosis via caspase-1 and -8 but not caspase-3 or -7 activation. These changes are prevented by GM-0111 treatment. IL-6 and -8 promote an inflammatory response in vivo through the recruitment of neutrophils and further inflammatory signaling in a positive feedback loop. The process of pro-inflammatory cell death is propagated to nearby cells due to these changes in the local environment, resulting in an unchecked cytotoxic response initiated by LL-37.