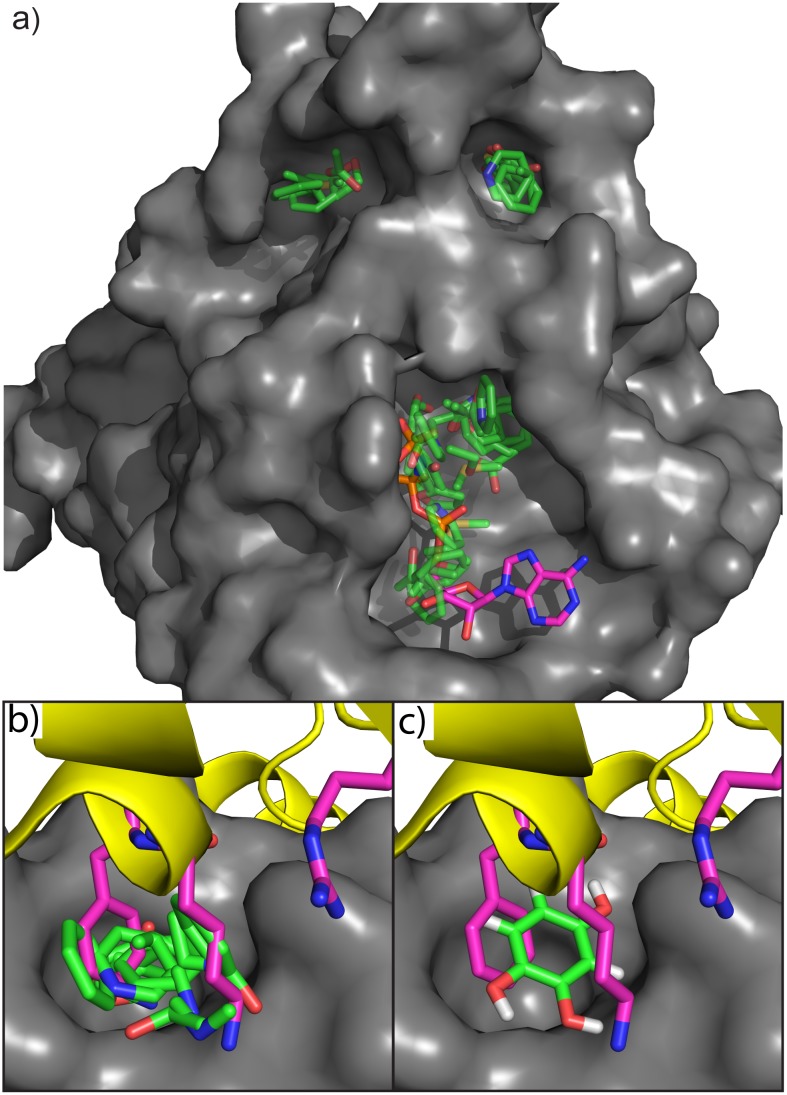
Fig 2. Hot spots on RecA.
a) Sites where a diversity of fragments simultaneously binds with high affinity and where no high affinity waters appear. The sites correspond to the ATP binding site (ATP is shown in magenta), an interaction site between RecA monomers (top right site), and the DNA binding site (upper left site). Three universally conserved residues (K216, F217, and R222) from the neighboring subunit (yellow ribbons) are shown with magenta carbons and the interactions at the RecA-RecA site for these residues are shown in (b). Mutations of these three residues will result in the loss of RecA function, although F217Y results in a 250-fold increase in the interaction between RecA subunits. SACP predicts that alkylamines bind in the RecA pocket mimicking K216 interactions (b) and that phenol mimics the F217 interaction. SACP also predicts that adding extra hydroxyl groups to the benzene ring results in a higher affinity (c). When the fragment patterns are combined, SACP creates 6-Hydroxydopamine in the RecA-RecA interaction site.