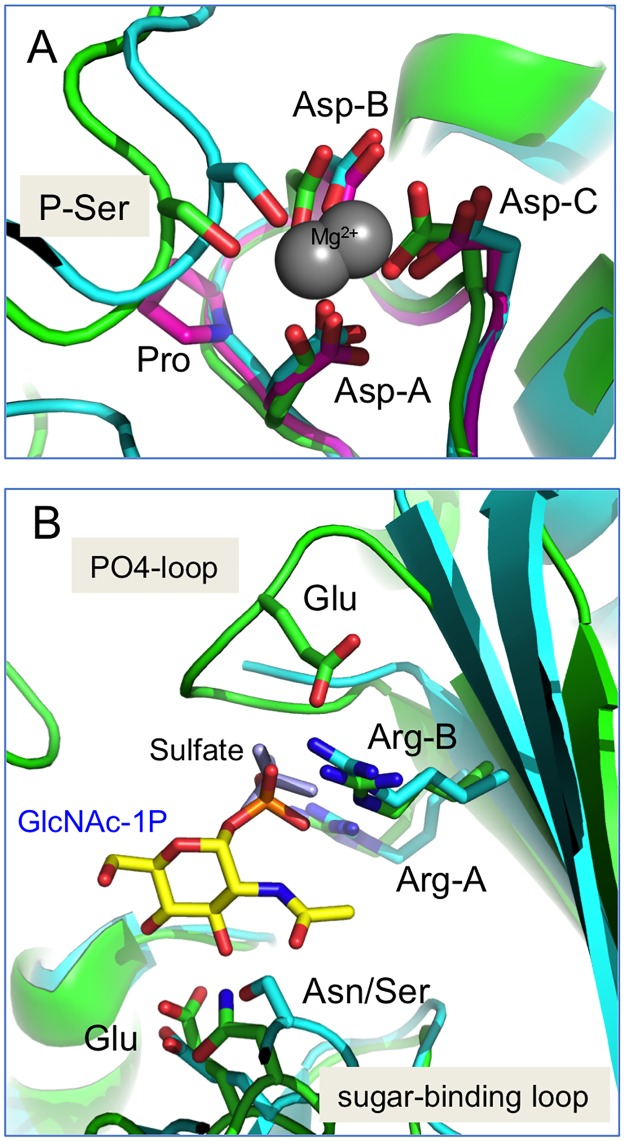
Fig 4. Close-up view of key active site regions of the PGM1 paralogs.
(A) The catalytic serine and metal-binding loop (regions i- ii) in a superposition of PGM1 (cyan), a PGM3 ortholog (green), and a related bacterial enzyme (PDB ID 2Z0F) (pink). The catalytic serine (shown in its dephospho-state) and the three conserved aspartates (Asp-A,B,C) that coordinate bound metal are highlighted. The bacterial enzyme has a metal-binding loop sequence equivalent to that of PGM2/2L1, and is included to show its structural similarity despite the proline between Asp-A and Asp-B. (B) The sugar-binding and PO4-binding loops (regions iii-iv) of PGM1 and the PGM3 ortholog. Colors as in (A). The bound substrate (N-acetylglucosamine 1-phosphate) from the enzyme-ligand complex in 2DKD is shown in yellow; bound sulfate ion in 5EPC is shown in light blue. In the sugar-binding loop, the conserved glutamate found in all paralogs, and the nearby Ser/Asn (PGM1 vs. PGM3) are labeled. In the PO4-binding loop, the two conserved arginines (Arg-A,B) found in PGM1/3/5 are highlighted, along with the conserved glutamate found in PGM2/2L1/3.