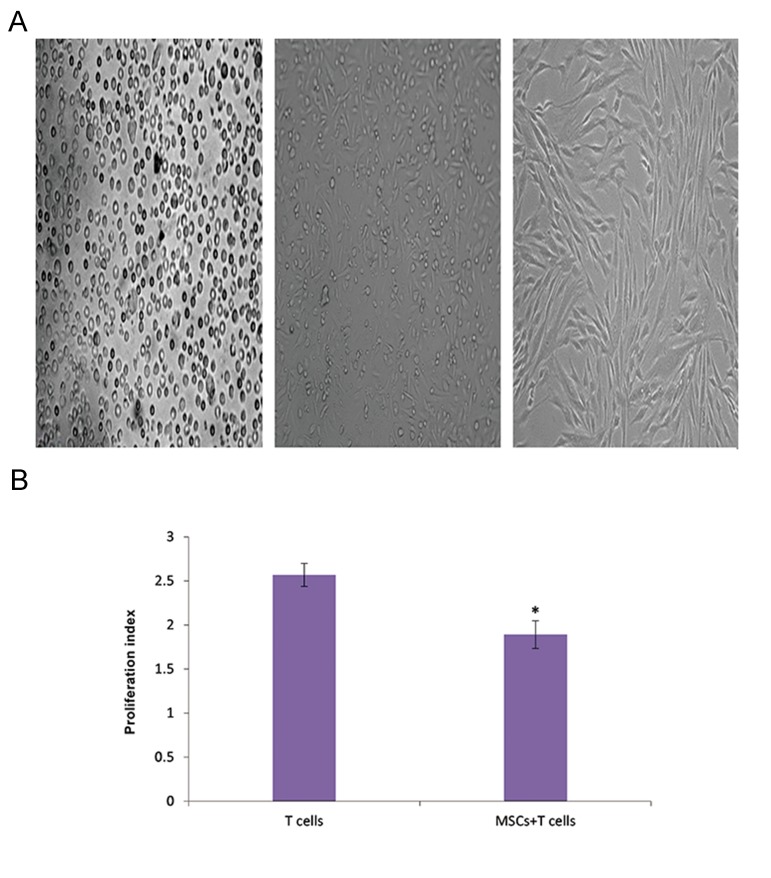
Fig.1.
Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). A. Representative fields depicted rat bone marrow-derived MSCs at different passages. Left: Initially, the isolated cells showed a round morphology. Middle: During the first sub-culture, MSCs exhibited diverse morphologies that included ovoid, bipolar and large, flattened morphology. Right: Sub-culture 3 of cells showed large, flattened or fibroblast-like morphology typical of MSCs and B. MSC-T cell co-culture: T cells were stimulated with phytohemagglutinin (PHA) or medium in the presence of MSCs (10 splenocytes to 1 MSC) or absence of either MSCs or MCs. After 5 days, we calculated the proliferation index (PI). *; P<0.01 vs. T lymphocytes without MSCs.