Figure 8. Schematic diagram of potential mechanisms that link bile acid and estrogen with H19-mediated cholestatic injury in female Mdr2−/− mice.
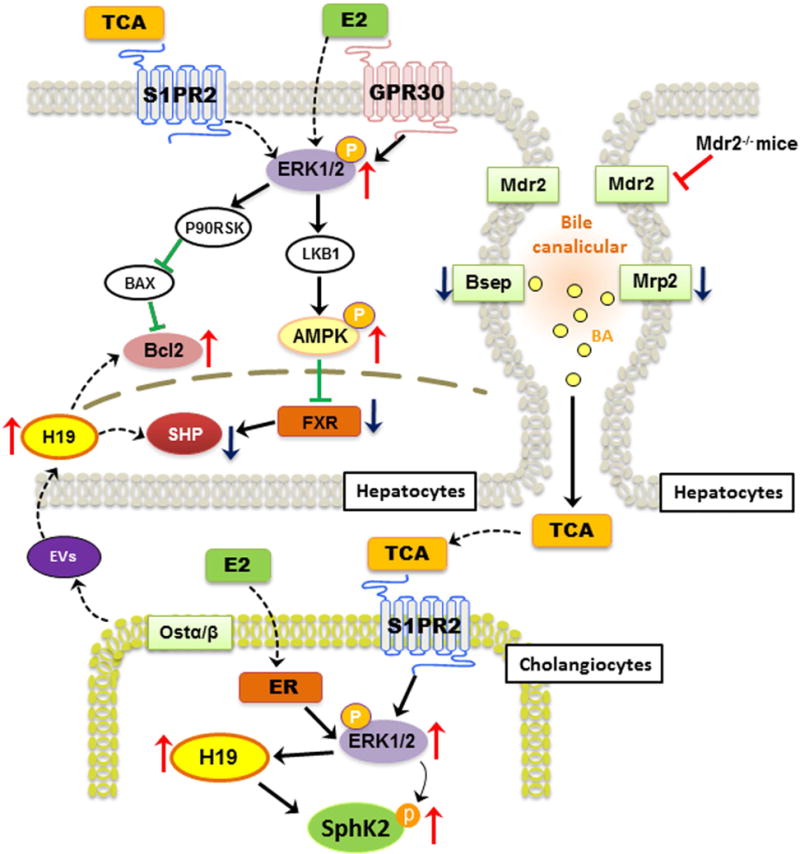
TCA-mediated activation of S1PR2 and estrogen-mediated activation of ER further induce activation of ERK1/2 both in cholangiocytes and hepatocytes. In cholangiocytes, both TCA and E2 up-regulate H19 expression, which further increases the expression of pro-fibrotic genes such as c-Myc, collagen I and Bcl-2. In hepatocytes, activation of ERK1/2 further induces phosphorylation of AMPK, which has been shown to inhibit FXR and SHP expression. In addition, the extracellular vesicles (EV) derived from cholangiocytes further downregulate SHP expression and disrupt bile acid homeostasis and ultimately cause hepatic cholestatic injury. H19 represents a potential candidate marker and a therapeutic target for cholestatic liver injury.
