Figure 6. Effect of PTX3 on monocytes and macrophages.
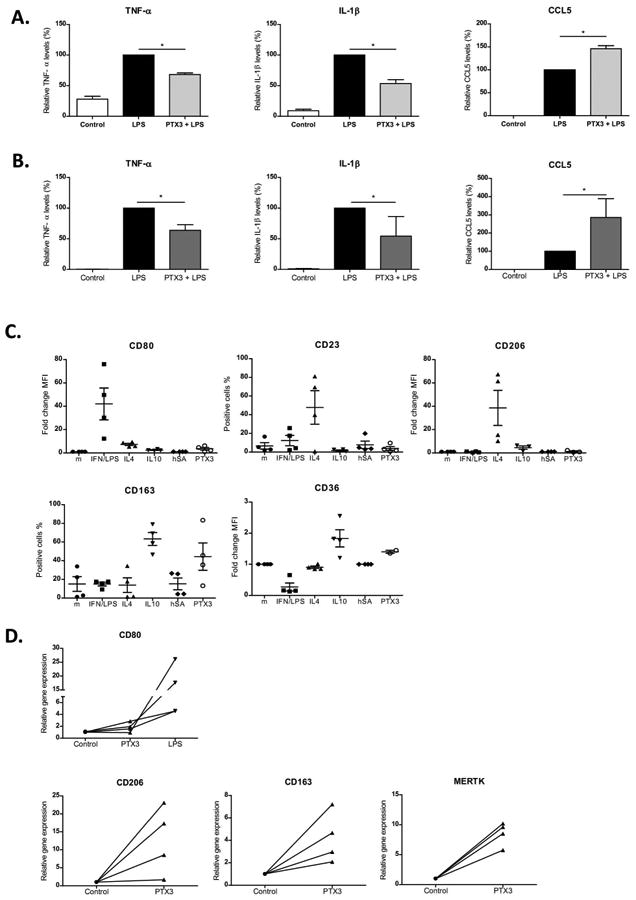
Peripheral blood monocytes isolated from healthy donors and human liver macrophages were incubated with rPTX3 followed by stimulation with LPS. a) human monocytes and b) human liver macrophages relative TNF-α, IL-1β and CCL5 levels in supernatant in the presence of LPS (10 ng/mL) and rPTX3 (1 μg/mL) compared with LPS (10 ng/mL) alone; n≥3 donors and patients. For normalization, cytokine production induced by stimulation with LPS of each experiment was set at 100; and relative cytokine production in the presence of rPTX3 or controls was calculated (*p<0,05). Peripheral blood monocytes isolated from four healthy donors were incubated (106 cells/well) during 3 days with INF/LPS (50/100 ng/mL), IL4 (40 ng/mL), IL10 (50 ng/mL), human albumin (hSA, 1 μg/mL) and rPTX3 (1 μg/mL) separately in RPMI with 5% FBS. c) Expression of macrophage polarization cell markers (CD80, CD23, CD206, CD163 and CD36) analyzed by flow cytometry (n=4). d) Human liver macrophages isolated from patients were incubated with rPTX3 (1 μg/mL). Gene expression of macrophages cell markers (CD80, CD206, CD163, Mertk) analyzed 24h after stimulation by real time PCR (n=4). As a positive control of CD80 (M1) induction liver macrophages were incubated with LPS (10 ng/mL).
