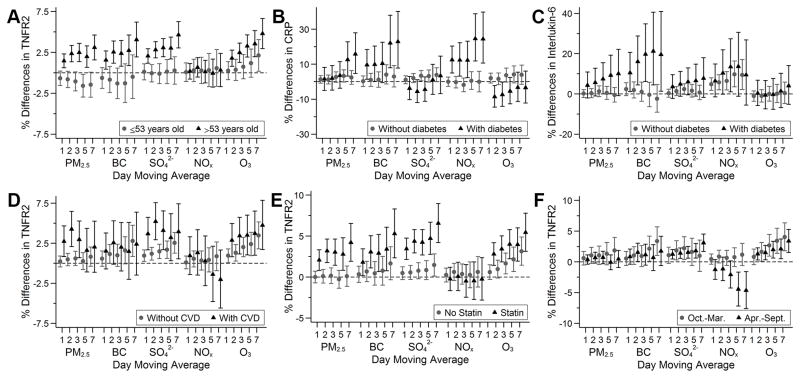
Figure 2.
Associations of 1- to 7-day moving averages of air pollutants with TNFR2 stratified by median age (A); with C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 stratified by diabetes status (B and C); and with TNFR2 stratified by season (D) among participants from the Framingham Offspring cohort examination 7 (1998–2001), examination 8 (2005–2008), Third Generation cohort examination 1 (2002–2005), and examination 2 (2008–2011). Models were adjusted for centered age, (centered age)2, sex, body mass index, smoking status, pack years, alcohol intake, educational attainment, census tract median household income, date of examination visit, sine and cosine season, day of week, temperature, and relative humidity. An exam identifier was added for CRP, interleukin-6, TNFR2, and fibrinogen. Results were scaled to 5 μg/m3 for fine particulate matter (PM2.5), 0.5 μg/m3 for black carbon (BC), 2 μg/m3 for sulfate (SO42−), 20 ppb for nitrogen oxides (NOx), and 10 ppb for ozone (O3). Error bars indicate the 95% confidence intervals.