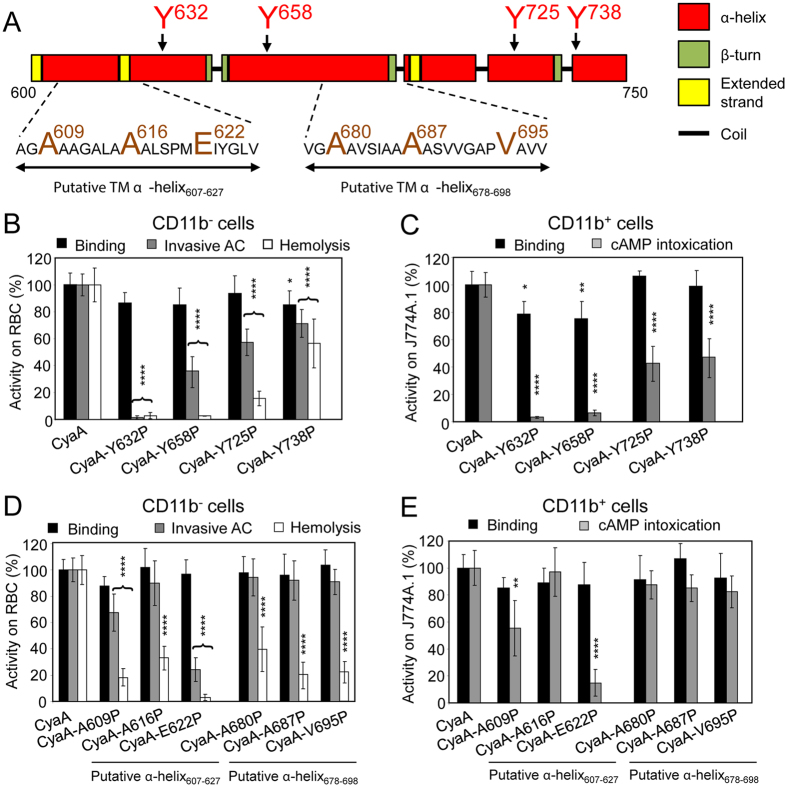
Figure 3.
α-helical structures located between residues 600 to 750 of CyaA participate in AC domain translocation and pore formation. (A) Schematic secondary structure of the segment 600 to 750 of CyaA with two putative transmembrane (TM) α-helices predicted by Eisenberg method64 and located between residues 607 to 627 and 678 to 698. The amino acid residues selected for substitution are enlarged and colored. (B to E) Biological activities of intact CyaA or its mutant variants were analyzed using CD11b− sheep erythrocytes (B,D) and CD11b+ J774A.1 mouse macrophages (C,E). Preparations and analyses of samples were performed as in the legend to Fig. 1. All activities are expressed as percentages of intact CyaA activity and represent average values ± standard deviations from at least three independent determinations performed in duplicate with two different toxin preparations. Significant differences are indicated by asterisks (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001).