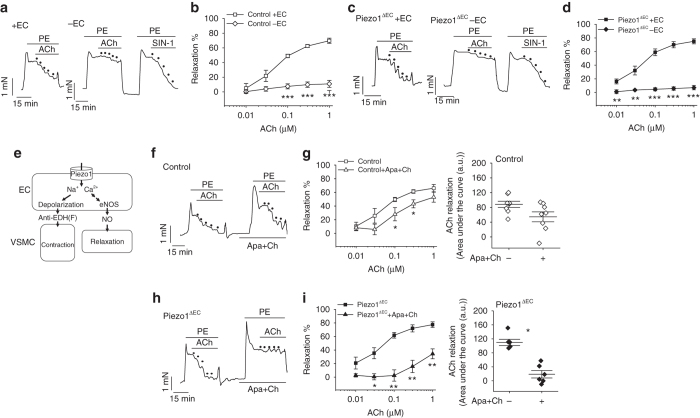
Fig. 2.
Endothelial Piezo1 channels have an anti-EDH(F) effect. Isometric tension recordings from mouse second-order mesenteric artery. a Example recordings from control genotype artery before (+ EC) and after endothelium-denudation (−EC). Upward deflection is increasing tension. Phenylephrine (PE, 0.3 μM). Acetylcholine (ACh) and the nitric oxide donor amino-3-morpholinyl-1,2,3-oxadiazolium (SIN-1) were applied at increasing concentrations as indicated by the dots (0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3 and 1 μM). b As for a but mean data (n = 14 mice). c, d As for a, b but Piezo1ΔEC mice (n = 10 mice). e Schematic illustration of the dichotomy Piezo1 presents for endothelial biology and vascular function. EC, endothelial cell. VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell. eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase. NO, nitric oxide. EDH(F), endothelium-derived hyperpolarization (factor). f Example recordings from control genotype artery before and after application of apamin (Apa, 0.5 μM) and charybdotoxin (Ch, 0.1 μM). Phenylephrine (PE, 0.3 μM). Acetylcholine (ACh) was applied at increasing concentrations as indicated by the dots (0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3 and 1 μM). g As for f but mean data (n = 8 mice). h, i As for f, g but for Piezo1ΔEC mice (n = 6 mice). Averaged data are displayed as mean ± s.e.m. Data sets are compared by t-test. Statistical significance is indicated by *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001