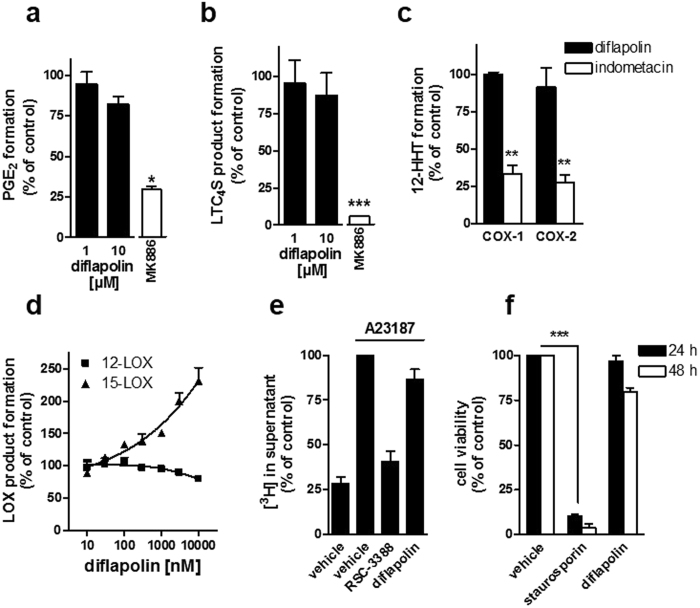
Figure 3.
Diflapolin shows target specificity within the AA cascade without cytotoxicity. (a) mPGES-1 activity. Microsomes of IL-1β-stimulated A549 cells were pretreated with diflapolin, 10 µM MK886, or vehicle for 10 min on ice and stimulated with 20 µM PGH2. After 1 min at 4 °C, PGE2 formation was analyzed by HPLC. (b) LTC4S activity. Microsomes of LTC4S-expressing HEK293 cells were pretreated with diflapolin, MK886 (10 µM), or vehicle for 10 min on ice with subsequent addition of LTA4-methyl ester. After 10 min at 4 °C, LTC4-methyl ester was analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS. (c) COX-1/2 activity. In cell-free assays, purified ovine COX-1 and recombinant human COX-2 were pretreated with diflapolin (10 µM), indometacin (10 µM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) for 5 min on ice and stimulated with AA (5 and 2 µM for COX-1 and -2, respectively for 10 min at 37 °C. 12-HHT was analyzed by HPLC. (d) Effect of diflapolin on 12- and 15-LOX. Intact neutrophils were pre-incubated by diflapolin or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) and stimulated with 2.5 µM Ca2+-ionophore plus 20 µM AA for 10 min at 37 °C. 12- and 15-HETE were determined by HPLC. (e) AA release. [3H]AA-labeled neutrophils were pretreated with diflapolin (1 µM), RSC-3388 (10 µM) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO) and stimulated by 2.5 µM Ca2+-ionophore for 15 min. Radioactivity of the supernatant was analyzed by scintillation counting. (f) Cell viability assay. Monocytes were treated with diflapolin (10 µM), staurosporin (3 µM) or vehicle (0.3% DMSO) for 24 and 48 h, respectively. Cell viability was determined by MTT assay. Data are expressed as percentage of control (100%), means + SEM, n = 3–5. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005; ***p < 0.001 vs. vehicle control (paired t-test).