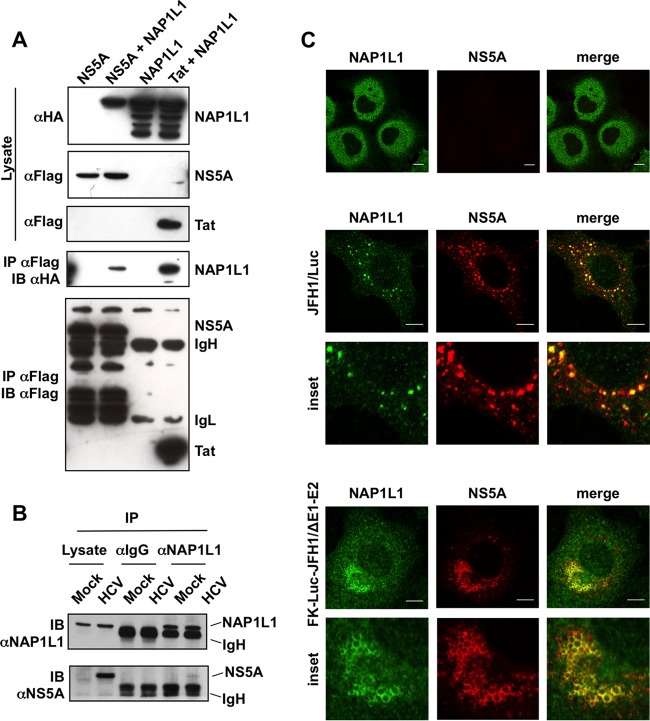
FIG 1.
HCV NS5A binds NAP1L1. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged NS5A and HA-NAP1L1 in HEK 293T cells. Transfected cells were lysed, coimmunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG–agarose beads, and blotted against anti-FLAG or anti-HA antibodies as indicated. A plasmid encoding HIV-1 FLAG-tagged Tat was used as positive control. IgL, immunoglobulin light chain; IgH, immunoglobulin heavy chain. (B) NS5A interacts with endogenous NAP1L1 during HCV replication. Huh7-Lunet cells were electroporated with subgenomic SGR-JFH1/Luc or mock transfected. At 72 hpe, cell lysates were incubated with anti-NAP1L1 antibodies or with matching irrelevant IgGs. Input and co-IP samples were then immunoblotted with anti-NAP1L1 and anti-NS5A antibodies as indicated. (C) NS5A and NAP1L1 colocalize during HCV replication. Huh7-Lunet cells were either mock electroporated or treated with the subgenomic HCV replicon SGR-JFH1/Luc or with SGR-FK-Luc-JFH1/ΔE1-E2 and fixed at 72 hpe. Indirect immunofluorescence analysis was performed with anti-NAP1L1 (green) and anti-NS5A (red) antibodies and corresponding fluorescent secondary antibodies (scale bars, 10 μm). Colocalization is shown in the merge channel (Pearson's correlation coefficients of 0.658 for SGR-JFH1/Luc and 0.731 for SGR-FK-Luc-JFH1/ΔE1-E2). The inset shows a high-magnification image. Diffused, cytoplasmic localization of NAP1L1 in mock-treated cells is also shown for comparison (top panels).