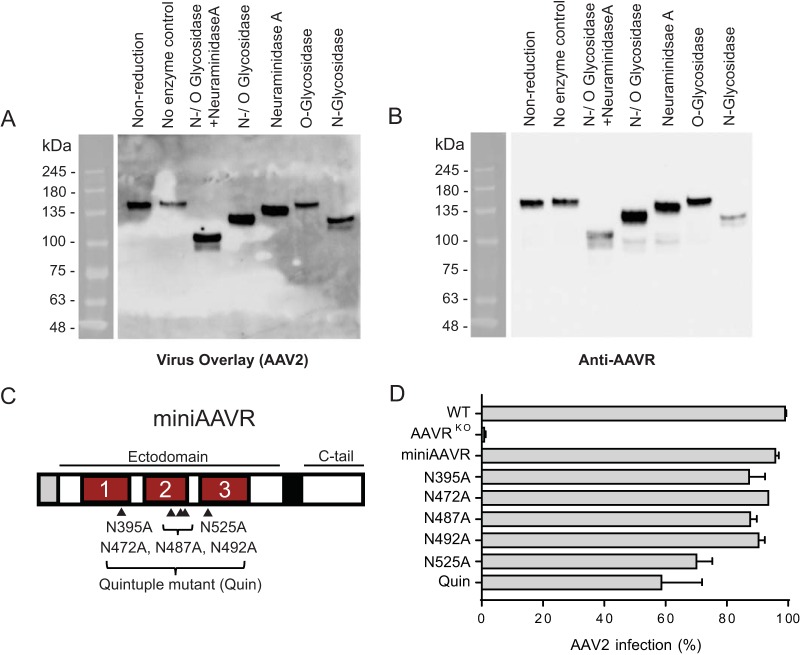
FIG 3.
AAVR glycosylation is not crucial for its interaction with AAV2. (A and B) Purified HeLa S3 membrane proteins were solubilized in PB–2% DMT. Twenty micrograms of the solubilized membrane proteins was treated with various N- and O-deglycosylation enzymes prior to undergoing gel electrophoresis (SDS–6% PAGE), which was followed by a virus overlay assay with rAAV (A) and then reprobing with an anti-AAVR antibody (B). (C) Schematic depicting miniAAVR (comprising only PKD domains 1 to 3 in its ectodomain) and its 5 N-glycosylation sites, which were mutated from asparagine (N) to alanine (A) to create 6 glycosylation mutants, including Quin (carries mutations in all five sites). (D) scAAV2-CMV-RFP transduction of HeLa AAVRKO cells stably expressing AAVR glycosylation mutants depicted in panel C (MOI of 20,000 vg/cell). Data in panel D depict means with standard deviations from triplicate transductions, where transgene expression was measured after 48 h.