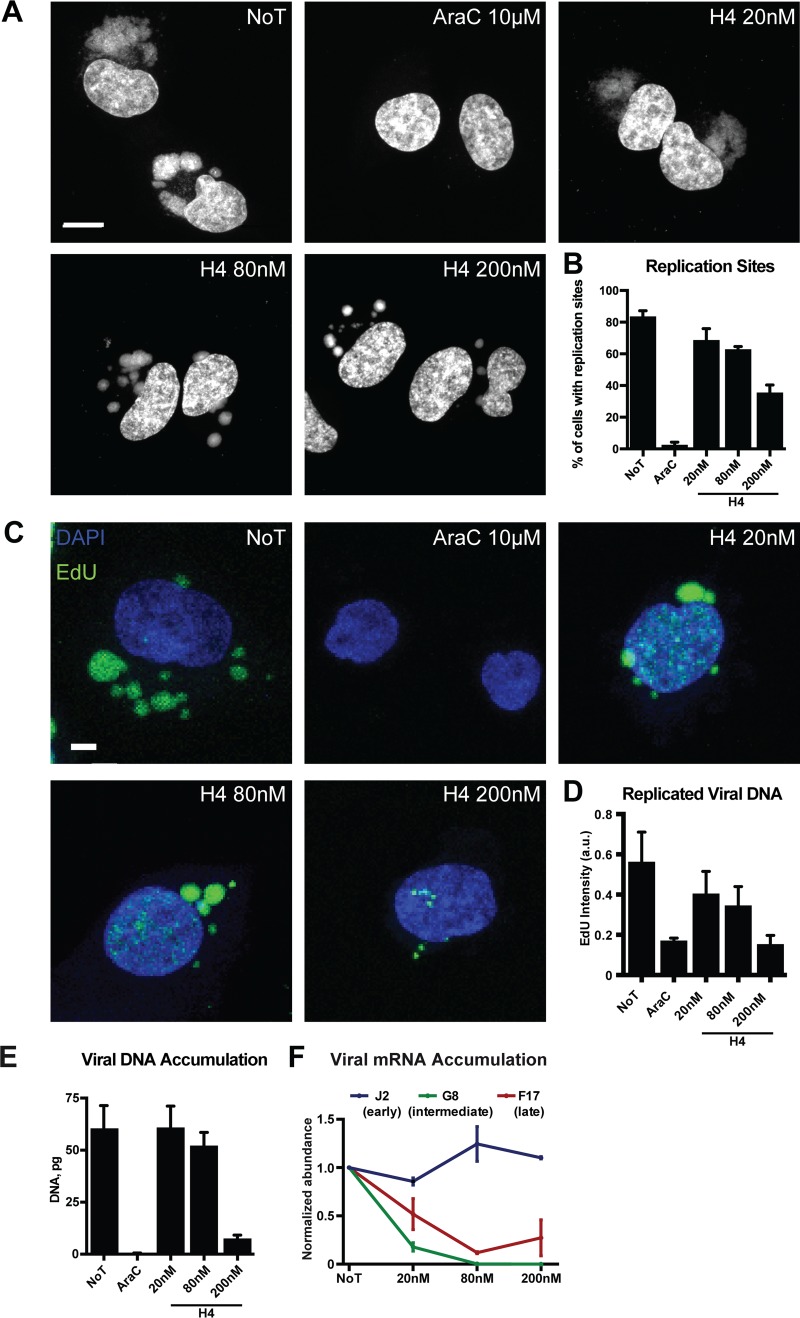
FIG 6.
H4 attenuates VACV IG/LG transcription and DNA replication in a dose-dependent fashion. (A) HeLa cells were infected (MOI of 10) in the presence of 20, 80, or 200 nM H4. At 8 hpi, cells were fixed and stained with DAPI and imaged by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) The number of cells with cytoplasmic replication sites was quantified per condition. AraC served as a control for inhibition of DNA replication site formation. (C) HeLa cells were infected (MOI of 10) in the presence of 20, 80, or 200 nM H4 and EdU. At 8 hpi, EdU incorporation was detected with a Click-iT EdU imaging kit followed by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) The total intensity of EdU incorporation into replication sites was quantified. (E) The amount of viral DNA from cells infected in the absence or presence of H4 at different concentrations was quantified by qPCR at 8 hpi. AraC served as a control for inhibition of DNA replication. (F) The levels of early (J2), intermediate (G8), and late (F17) viral mRNA from infected HeLa cells were quantified by RT-qPCR. Cells were infected in the absence or presence of various concentrations of H4, and RT was performed at 2 hpi for J2, 4 hpi for G8, and 8 hpi for F17. Results are displayed as the average abundance normalized to untreated samples. All experiments were performed in triplicate; representative images (A and C) or means ± SD (B and D to F) are displayed.