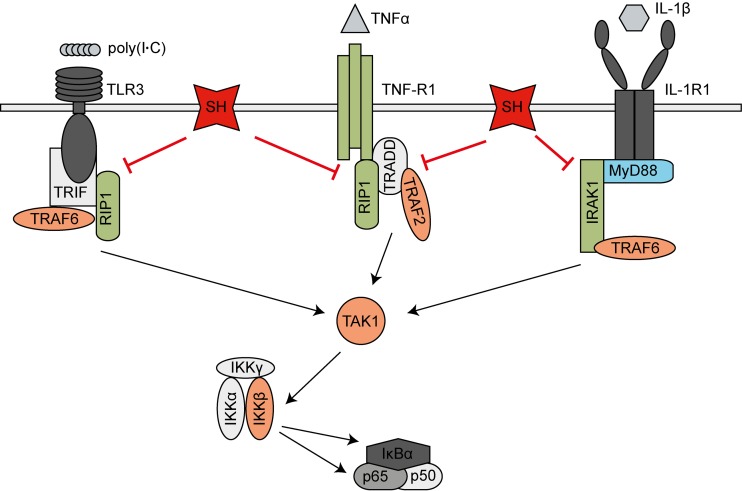
FIG 7.
Model of MuV SH interference with NF-κB activation. SH expression leads to a reduction of MuV-induced IKKβ, IκBα, and p65 phosphorylation and p65 translocation into the nucleus, resulting in decreased activation of NF-κB-controlled genes. Luciferase reporter gene assays revealed that SH (red) impacts NF-κB activation downstream of or at the level of MyD88 (blue) and upstream of TRAF2, TRAF6, TAK1, and IKKβ (orange) in the respective pathways. As SH was shown to interact with TNFR1, RIP1, and IRAK1 (green), we assume that SH inhibits NF-κB activation by interacting with the receptor complexes of TNFR1, IL-1R1, and TLR3 in the plasma membranes of infected cells.