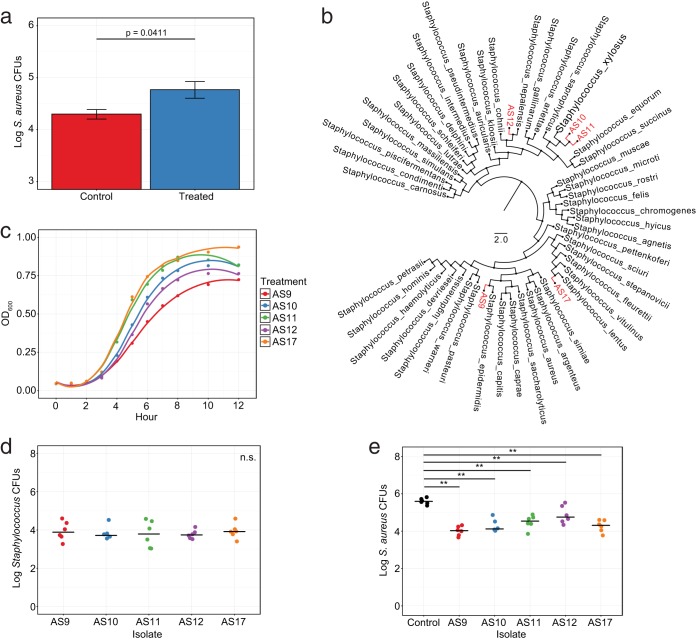
FIG 5.
Resident Staphylococcus can reduce colonization by Staphylococcus aureus. (a) Staphylococcus aureus CFUs following exogenous administration in mice pretreated with alcohol or in untreated controls. (b) Phylogenetic tree of 16S rRNA gene diversity using approximate-maximum-likelihood to compare murine Staphylococcus residents (red) to known Staphylococcus isolates from the RDP database (black). (c) Growth curve analysis of resident Staphylococcus isolates at an optical density of 600 nm (OD600). (d) Enumeration of Staphylococcus isolate CFUs following exogenous administration to mouse dorsa. (e) S. aureus CFU levels following precolonization of mouse dorsa with resident Staphylococcus isolates. Data are presented as means ± SEMs (a) or with median bars (d, e). Statistical significance was determined by Wilcoxon rank sum test (Mann Whitney U test). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.