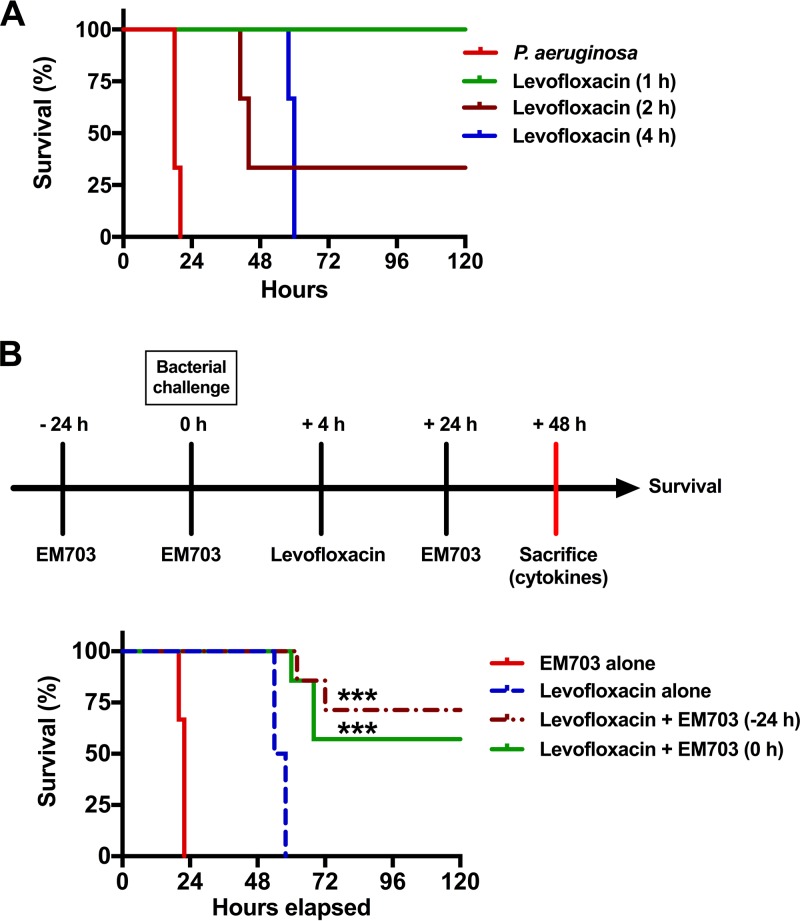
FIG 1.
Survival times for P. aeruginosa airway infections with combined treatment with levofloxacin and EM703. (A) Survival graph. The survival of levofloxacin-treated mice infected with P. aeruginosa (2 × 109 bacterial CFU) was monitored for 7 days (only the course during the first 120 h is shown). Levofloxacin (100 mg/kg) was administered subcutaneously 1, 2, or 4 h after infection. The graph shows one representative experiment of three, with three mice in each group. (B) Schematic overview of the experimental design and time points (upper), using levofloxacin to treat P. aeruginosa-infected mice in the absence or presence of EM703, and survival graph (lower) showing the effect of EM703 treatment on the survival of infected mice treated with levofloxacin (seven mice in each group, in two separate experiments). Treatment with EM703 (either 24 h prior to or simultaneously with infection) in combination with levofloxacin (initiated 4 h after infection) improved survival. EM703 alone did not affect the survival of infected mice that did not receive levofloxacin. Statistical comparisons of survival curves were performed using the Mantel-Cox test, comparing the group treated with levofloxacin alone and the groups treated with a combination of levofloxacin and EM703. ***, P ≤ 0.001.