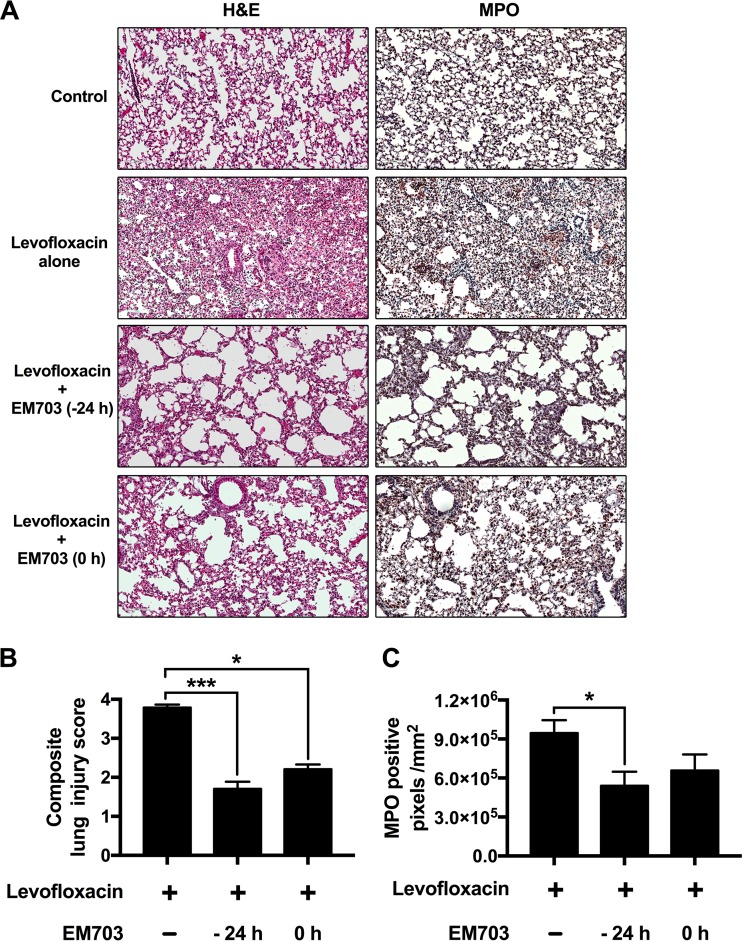
FIG 2.
Lung injury and numbers of neutrophils in lung tissue after EM703 pretreatment. (A) To investigate tissue damage and neutrophil infiltration, lung tissues were stained with H&E or processed for immunohistochemistry and stained to detect MPO. Dense infiltration of immune cells, alveolar thickening, and edema were seen in mice treated with levofloxacin alone, while the addition of EM703 (either 24 h before or at the time of infection) resulted in less pronounced changes. A high degree of neutrophil infiltration in mice treated with levofloxacin alone and less infiltration after the addition of EM703 were confirmed by immunohistological detection of MPO. (B) Blinded evaluation of tissue injury was performed using a lung injury scoring system and showed a significant reduction of lung injury after the addition of EM703 to levofloxacin treatment. (C) Quantification of MPO staining was performed with sections of lung tissue from 10 animals in each group. The results are expressed as the mean ± SEM (eight mice in each group). The Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test, with Dunn's post hoc test for multiple comparisons, was used. *, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001.