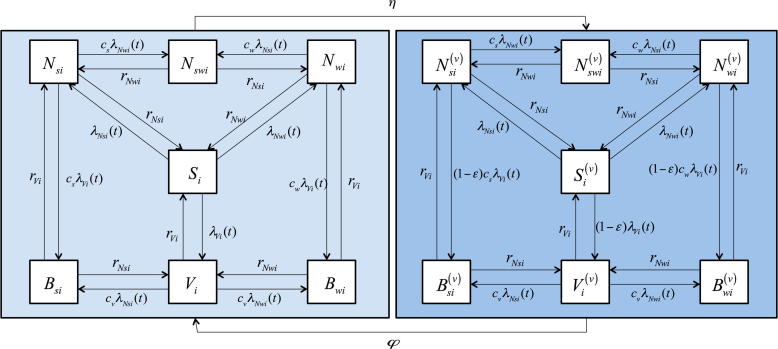
Fig. 1.
Model structure flow diagram. The epidemiological states include individuals that are susceptible (non-carrying), ; carry a vaccine serotype, ; carry a weak non-vaccine serotype, ; carry a strong non-vaccine serotype, ; carry simultaneously a weak and a strong non-vaccine serotype, ; carry simultaneously a vaccine serotype and a weak non-vaccine serotype, ; or carry simultaneously a vaccine serotype and a strong non-vaccine serotype, (see text). Once vaccinated, the individual moves to one of the corresponding states, . The acquisition rates from the single to multiple serotype carriage states are reduced by competition parameters denoted by with two subscripts; the first denoting the serotype group (, for VT, strong NVT and weak NVT respectively) of the resident serotypes and the second denoting the age-group. The competition parameters have two sets of values, one for age group <6 and another for age group ≥6 years (see text). The age-group specific VT, weak NVT and strong NVT clearance rates are denoted by and , respectively. In addition to the transitions between the 14 epidemiological states as shown in the figure, individuals die from any states at age-specific death rates and new individuals are born into the completely susceptible state.