Figure 1.
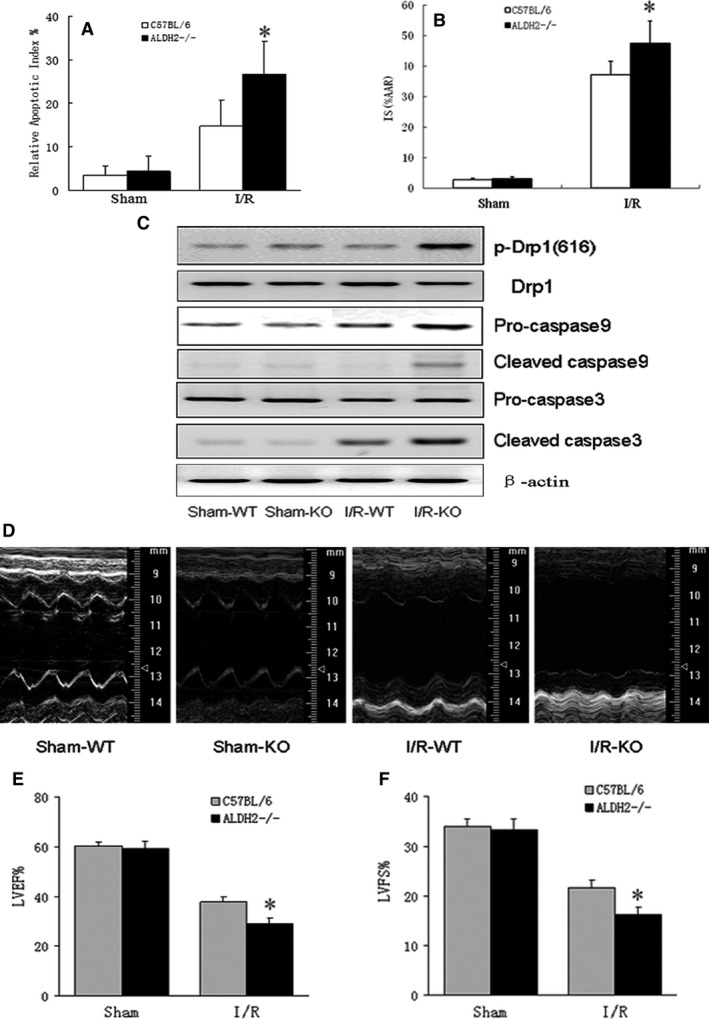
I/R‐induced increased myocardial infarct size and cardiomyocyte apoptosis in ALDH2−/− mice. Hearts from ALDH2−/− mice and wild‐type (WT) littermates were subjected to 45‐min. ischaemia and followed by 24 hrs of reperfusion, then mice were killed and the cross sections of hearts were sliced and examined by the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase‐mediated dUTP nick‐end labelling (TUNEL) staining. (A) Apoptotic Index was quantified by counting TUNEL‐positive cells nuclei from 10 random fields per section in the border zone of area at risk from left ventricular tissue and was expressed as a percentage of total myocyte nuclei. (B) Myocardial infarct size was calculated by the percentage of infarct size (IS) versus area at risk (AAR). (C) The mitochondrial levels of phosphorylated Drp1 and caspase9 were determined by Western blot. (D–F) Representative M‐mode tracings of mice and echocardiographic parameter analysis for left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and left ventricular fraction shortening (LVFS), all data were presented as mean ± SD. n = 5–6, *P < 0.05, vs C57BL/6 mice post‐I/R.
