Figure 1.
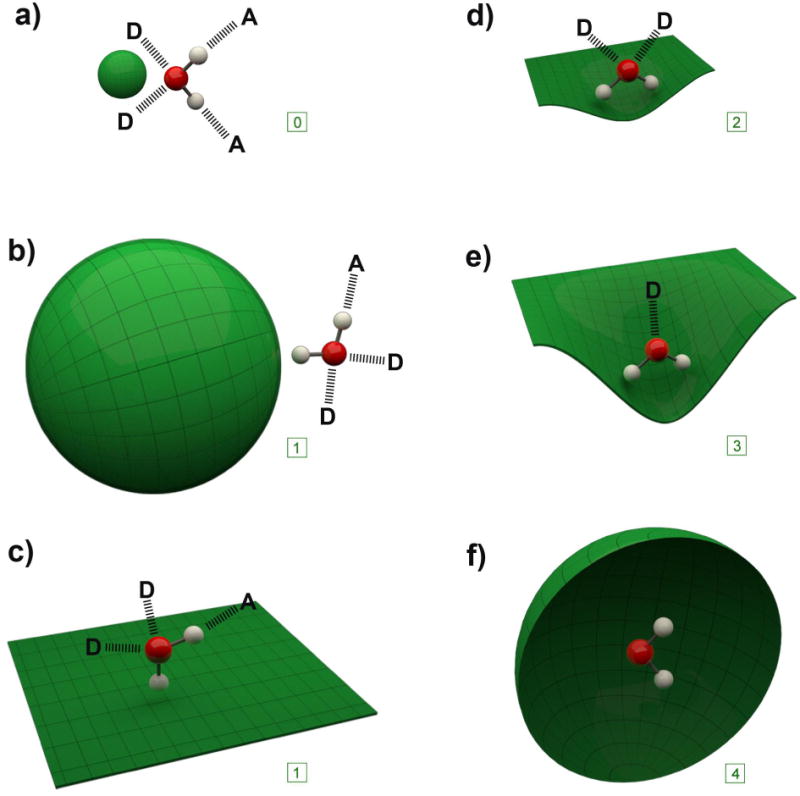
Idealized representations of the solvation of the surfaces discussed in this review. For each of the six cases one water molecule is shown along with the idealized number of HBs to donor (D) or acceptor (A) water molecules in the solvation shell. For each case, the corresponding number of dangling HBs is shown in the box: a) a small convex solute; b) a large convex molecule; c) a flat surface; d) a slightly concave surface; e) a highly concave surface; f) a fully encapsulating surface (front hemisphere removed for visualization).
