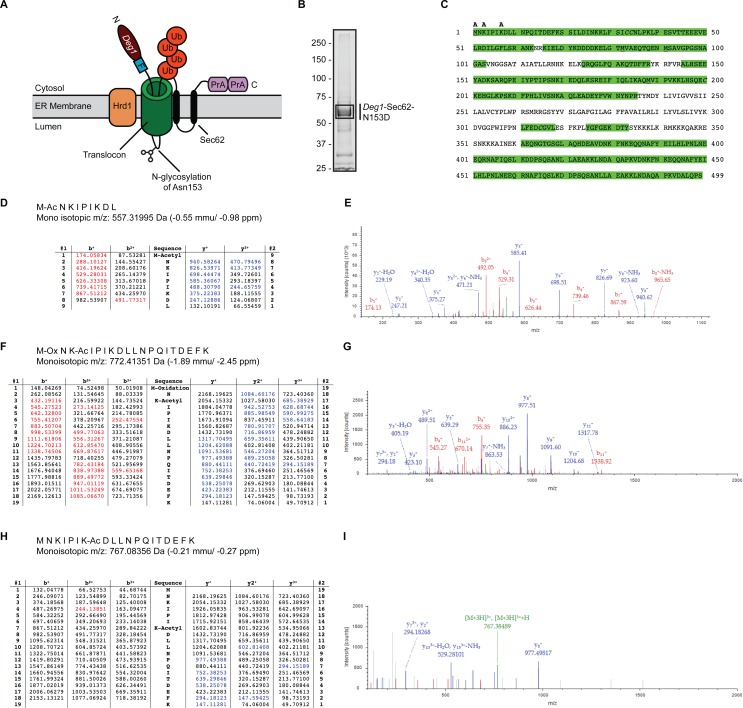
Figure 1. Acetylation of Deg1-Sec62-N153D.
(A) Schematic of Deg1-Sec62 following aberrant translocon engagement. Deg1-Sec62 possesses, in sequence, Deg1 (the N-terminal 67 amino acids from the yeast transcriptional repressor MATα2), a Flag epitope (F), the two-transmembrane protein Sec62, and tandem copies of Protein A (PrA) from Staphylococcus aureus. Following co-translational insertion of the two transmembrane segments of Sec62 (black ovals), a portion of the cytosolic N-terminal tail aberrantly moves into the translocon via the post-translational translocation mechanism. Aberrant translocation is followed by N-linked glycosylation of Asn153 and Hrd1-dependent ubiquitylation (Rubenstein et al., 2012). (B) Purification of Deg1-Sec62-N153D. Deg1-Sec62-N153D was immunoprecipitated from lysates of hrd1Δ cells, separated by SDS-PAGE, and stained with GelCode Blue. Bands corresponding to Deg1-Sec62-N153D (demarcated by box) were excised, subjected to in-gel digestion, and evaluated by LC/ESI MS/MS. (C) Peptide map of Deg1-Sec62-N153D. High confidence peptide identifications from SEQUEST-HT (false discovery rate < 1%) were mapped to the Deg1-Sec62-N153D protein sequence. Regions highlighted in green are segments of the amino acid sequence identified by MS. Amino acids identified as acetylated are labeled “A”. Underlined amino acids represent detection of methionine oxidation, a likely artifact of electrospray MS (Chen & Cook, 2007). Italicized amino acids represent cysteine residues modified by carbamidomethylation following iodoacetamide treatment. (D–I) Tandem mass spectra of proteolytically digested Deg1-Sec62-N153D were subjected to acetylpeptide identification using the database search algorithm SEQUEST-HT (part of Proteome Discoverer). The tables (D, F, H) display predicted fragment ions for the identified peptides and highlight in red and blue the b-and y-ions, respectively, identified in the fragment spectra (E, G, I). Red and blue peaks in the fragment spectra reflect tandem MS data that matched theoretical peptide fragment masses listed in the tables. Green peaks represent precursor ions or precursor ions with a neutral loss of water or ammonia. N, Amino terminus. C, Carboxyl terminus. Ub, ubiquitin. Ac, acetylation. Ox, oxidation.