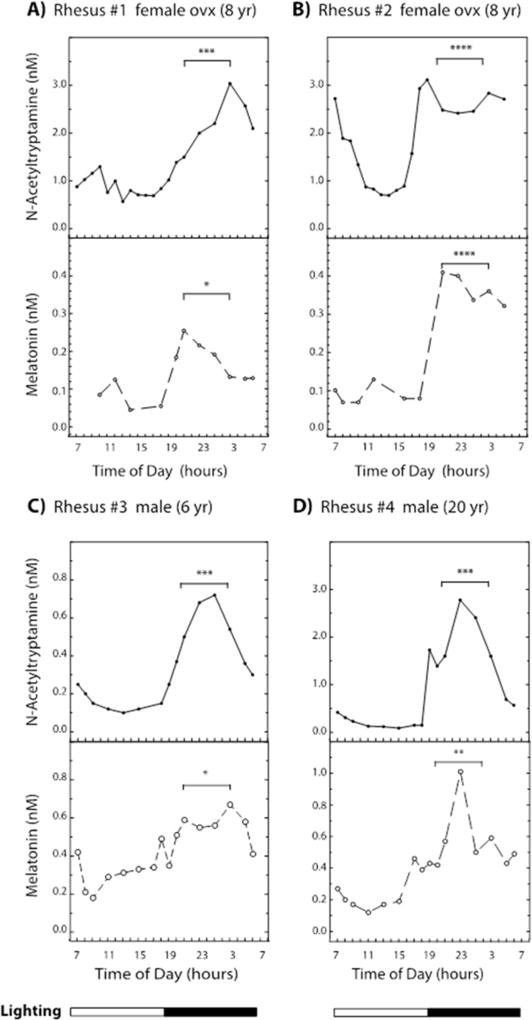
Figure 4. Daily changes in plasma N-acetyltryptamine and melatonin in the rhesus macaque.
Blood was obtained continuously in ten to thirty minute fractions over a 25 hour period remotely from animals that were undisturbed, conscious and unrestrained (Urbanski 2011). Animals were exposed to 12 h of light followed by 12 h of dark over the 24 hour period, with lighting on from 07:00 h to 19:00 h. N-Acetyltryptamine and melatonin levels were determined for two ovariectomized (OVX) females (A & B) and two males (C & D); sequential day samples were pooled to increase the melatonin signal strength to detectable levels. Mean plasma values during 6-hour periods of the night (21:00 h to 03:00 h) and day (09:00 h to 15:00 h) were significantly different (P values: * = 0.01 to 0.05, ** = 0.001 to 0.01, *** = 0.0001 to 0.001, **** < 0.0001). Additional experimental details appear in the Materials and Methods section.