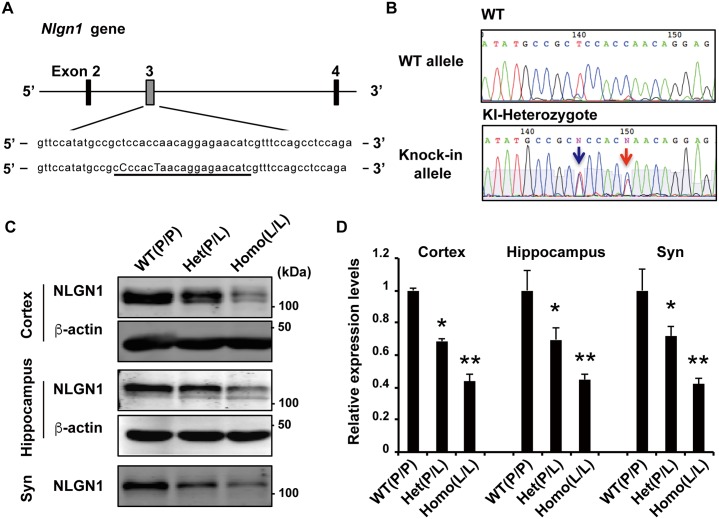
Fig 5. Generation of Nlgn1 P89L KI mice.
(A) Schematic of the mouse genomic locus of Nlgn1 showing the target site of Cas9. sgRNA sequence is underlined, and replaced bases in knock-in mice are capitalized. (B) DNA sequence electropherograms of WT and knock-in heterozygote mouse. Red arrow indicates the amino acid substitution from proline to leucine (CCA to CTA of residue 89), and blue arrow indicates a silent mutation for genotyping using restriction enzyme BsrBI. (C-D) Western blots of cortex, hippocampus, and cortical synaptosomal fractions from wild-type, Nlgn1 P89L heterozygote, and homozygote mutant mice. (WT n = 3, heterozygote n = 4, homozygote n = 3) Data are represented as means ± S.E.M. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01 Tukey-Kramer’s multiple comparisons test).