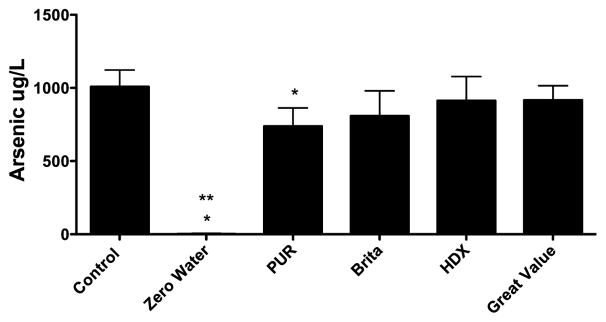
Figure 3.
The ability of five tabletop water pitcher filters, listed by the brand name, to remove arsenic (1,000 μg/L) from soft water. Control represents ICP-MS measurements of the arsenic solution before it was added to the filters. Three lots of each filter were tested, 1 L/filter. *P<0.05 versus 1,000 μg/L **P<0.001, indicates that the ZeroWater® filter reduced the arsenic concentration in the filtrate to less than 10 μg/L (mean 2.63 μg/L ± 2.06 μg/L). Data presented as the mean ± SEM. Effluent arsenic concentrations were: ZeroWater® (2.7 ± 2.0 μg/L, 99.7% removed by filtration), PUR® (737.7 ± 72.4 μg/L, 26.2% removed by filtration), Brita® (808.2 ± 99.2 μg/L, 19.2% removed by filtration), HDX® (913.5 ± 95.0 μg/L, 8.7% removed by filtration), and Great Value® (916.8 ± 56.8 μg/L, 8.3% removed by filtration).