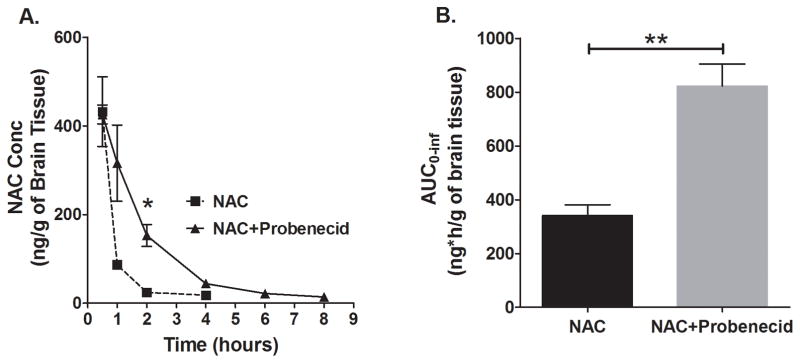
Figure 2.
NAC brain concentration–time profile and total brain exposure (AUC) of NAC, with or without co-administration of probenecid. Sprague-Dawley rats were administered a dose of either NAC (163 mg/kg) alone or in combination with probenecid (150 mg/kg) intraperitoneally and brain hemispheres were collected at several time points for NAC analysis. (A) Probenecid increased NAC brain concentrations starting from 1 h up to the 4 h time point. NAC levels were measurable until the last sampling time (8 h) in the group that received both NAC and probenecid, but were below limit of quantification at 6 h and 8 h in the group that received NAC only (mean±SEM, n=4 per time point, *p<0.05). (B) Probenecid increased brain AUC0–inf of NAC 2.46-fold (mean±SEM; p<0.01).