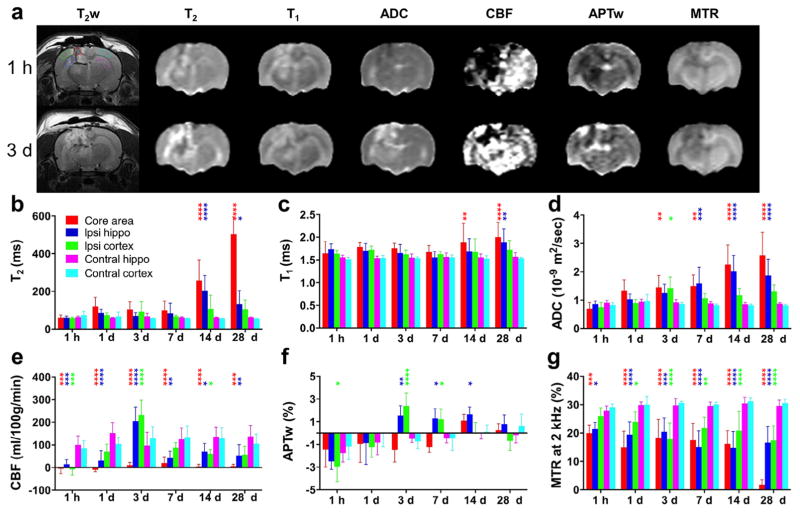
Fig. 1.
Quantitative multiparametric MRI assessment of traumatic brain injury (TBI) in rats. (a) Representative multiparametric MRI images in a rat at 1 h and 3 days after TBI. The five regions of interest (ROIs) are marked by dotted lines on the upper left T2-weighted (T2w) image. (b–g) Plots of MRI signal intensities in all five ROIs, acquired at 1 h and 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 days after TBI (n = 13). All MRI parameters were sensitive for detecting TBI at some time points. Notably, APTw and CBF MRI showed relatively large changes at 3 days post-TBI in ipsilateral perilesional areas, compared with those in corresponding contralateral brain areas. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 versus the corresponding contralateral brain areas.