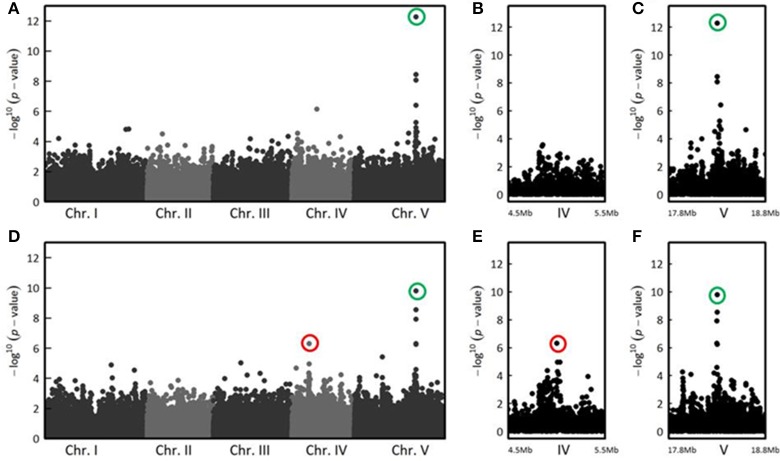
Figure 3.
The genetics of quantitative disease resistance to R. solanacearum GMI1000 strain at 27°C, identified by GWA mapping at 13 dai in the CUT and UNCUT conditions of inoculation. Whole genome scan of 214,051 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for association with disease index at 13 dai across 152 accessions that have germinated for which roots have been cut (A). Zoom showing the absence of QTLs of resistance in the CUT condition of inoculation on the chromosome IV, compared with the UNCUT condition thereafter (B). Zoom spanning a genomic region on the chromosome V from 17.8 to 18.8 Mb containing the QTL of resistance located in the RPS4/RRS1 locus (C). Whole genome scan of 214,051 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) for association with disease index at 13 dai across 163 accessions that have germinated for which roots remained uncut (D) and focus on two genomic regions corresponding to two QTLs of resistance observed on chromosomes IV (D) and chromosome V (E). The red circle indicates the top SNP (SNP-4-5080256, P = 4.93 × 10−7, MARF = 0.429) corresponding to a QTL of resistance detected at the beginning of chromosome IV in the UNCUT condition. The green circles highlight the top SNPs corresponding to the major QTL of resistance detected on the long arm of chromosome V in the UNCUT (SNP-5-18325032, P = 5.37 × 10−13, MARF = 0.125) and CUT (SNP-5-18325565, P = 1.60 × 10−10, MARF = 0.252) conditions.