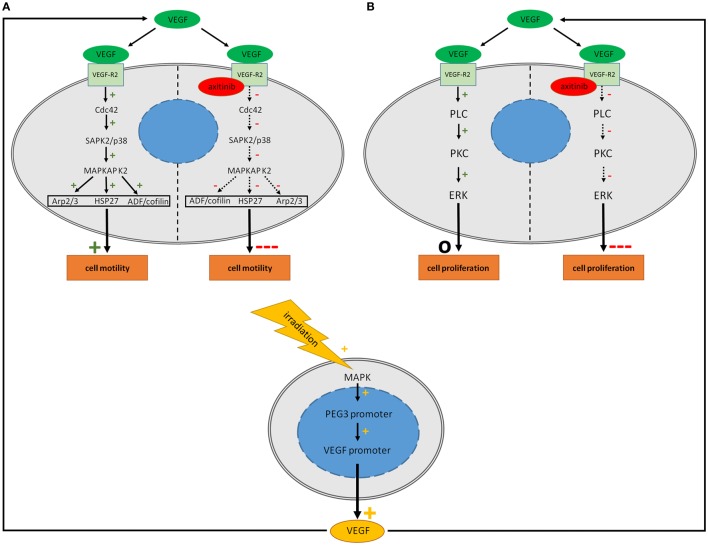
Figure 4.
Potential signaling in human glioblastoma cell lines after treatment with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), irradiation and axitinib. VEGF activates multiple pathways including the Cdc42 and PLC pathways concerning cell migration and proliferation. It is supposed that stimulating effects of irradiation are mediated via enhanced synthesis of VEGF. Irradiation elevates VEGF biosynthesis of glioblastoma multiforme cells via MAPK activation. (A) Activation of the Cdc42 pathway by VEGF leads to an increased activation of Arp 2/3, HSP27, and ADF/cofilin resulting in an enhanced motility. Blockade of the VEGF-R2 by axitinib might decrease the activation of the Cdc42 pathway due to theoretical consideration resulting in a crucial decreased cell motility. (B) VEGF activates the PLC pathway which is involved in cell proliferation while axitinib might deactivate this pathway with impairment of cell proliferation. While motility is increased by VEGF, no positive effect on proliferation could be observed. This might be due to fully activated VEGF-pathways even under control conditions. Continuous arrows: evidence of the effect, dotted arrows: assumption of the effect.