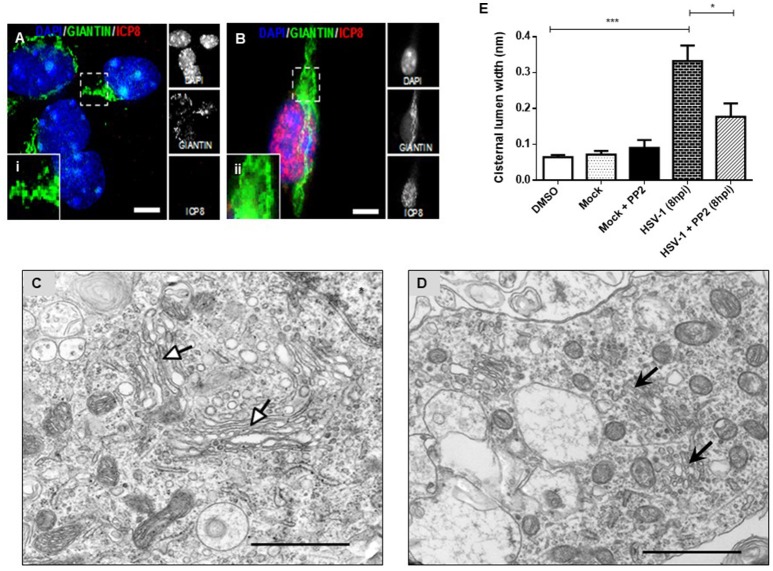
Figure 4.
PP2, a specific Src kinase inhibitor, reduced Golgi apparatus alterations observed during HSV-1 neuronal infection. Cortical primary neurons were treated with 20 μM PP2 for 12 h, then cells were left either mock-infected (A; MOCK) or HSV-1- infected (B) during 8 h in the presence of the inhibitor. After, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and immunostained for Giantin (Golgi marker, green) and ICP8 (viral infection marker, red). Nuclei were visualized with DAPI. (A,B) Show the corresponding merged images. (A,B) Show boxes (i–ii) with higher magnification indicating normal distribution of Giantin. Scale bar, 5 μm. Representative electron micrographs of Golgi stacks in mock-infected neurons (C) and in HSV-1 infected neurons at 8 hpi (D), both treated in the presence of PP2. Black arrowheads indicate that in the presence of PP2 there is a consistent reduction of the disrupted Golgi cisternae flatness and morphology trigger by HSV-1, observing similar results than in MOCK cells (white arrowheads). Asterisk indicated nucleus. Scale bar, 1 μm. (E) Quantitation of Golgi cisternae lumen (μm) in mock- and HSV-1- infected cells in the absence or presence of 20 μM PP2 for 12 h. In addition, treatment with 20 μM PP2 alone and DMSO vehicle control was also included. Data represents the average maximum luminal width of Golgi cisternae. Bars represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05. Brackets display treatment comparisons.